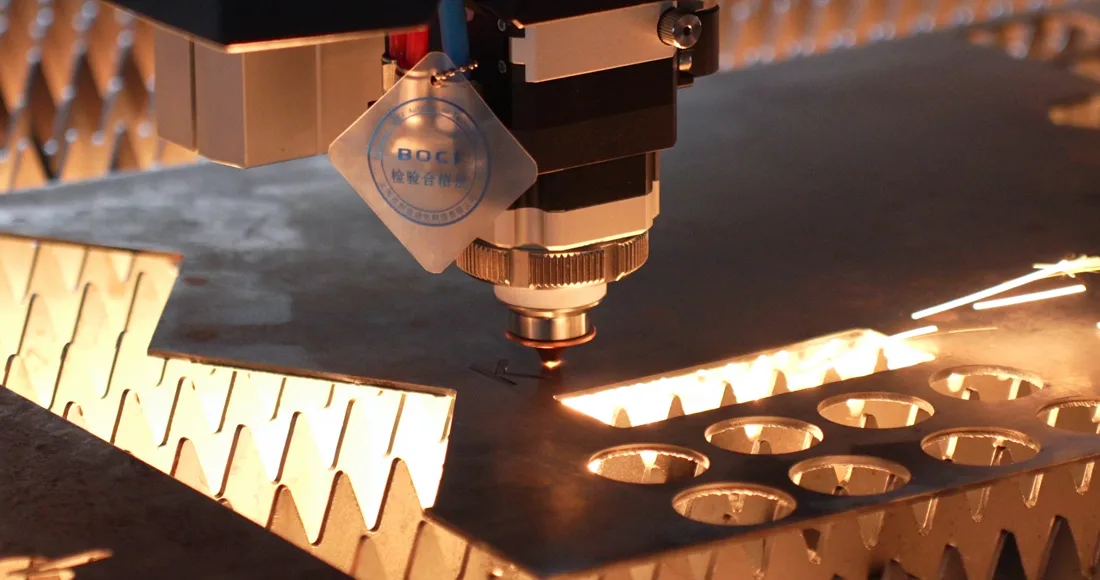
Have you ever wondered about fiber laser cutting advantages? What makes fiber lasers stand out, and how can they enhance your manufacturing processes? You're in the right place! Let's explore the remarkable benefits of fiber laser cutting and how it can revolutionize your operations.
Key Fiber Laser Cutting Advantages You Need to Know
- Versatility Galore: Fiber lasers are like the Swiss Army knives of the manufacturing world. They're used in almost every sector you can think of - from aerospace and automotive (even in e-mobility) to dental, electronics, jewelry, medical, science, semiconductor, sensor systems, solar, and more! It's like they have a little something for everyone.
- Space-Saving Wonders: These lasers are super compact and don't take up much space at all. If you're working in a place where space is tight, fiber lasers are your new best friends. They fit right in and get the job done without hogging all the room.
- Material Masters: Fiber lasers can manage a vast variety of materials. Metals are their bread and butter - think mild steel, stainless steel, titanium, and those tricky reflective ones like aluminum and copper. But that's not all! They can also work their magic on plastics, ceramics, silicon, and textiles. It's like they have a material superpower!
- Cost-Cutting Champions: If you're looking to save some bucks, fiber lasers are the way to go. They're a great value for your money with a good price/performance ratio. And get this - their maintenance costs are super low. So, you can keep your overheads and operating costs in check.
- Easy Integration: With a bunch of different interfaces, MAX fiber lasers are a breeze to add to your existing machines and systems. Whether you're an OEM or need a complete solution (laser, optics, sensor systems, and service), we've got your back.
- Energy-Efficient Stars: Fiber lasers are like the energy-saving heroes of manufacturing. They use way less power than those old-school manufacturing machines. This means you're not only reducing your carbon footprint but also saving on those pesky operating costs.
And do you know what? Taking all the above advantages into consideration, the full range of fiber laser cutting machines produced by KRRASS all use MAX fiber lasers. They really know how to make the most of these great fiber lasers!
How Fiber Lasers Work Their Magic
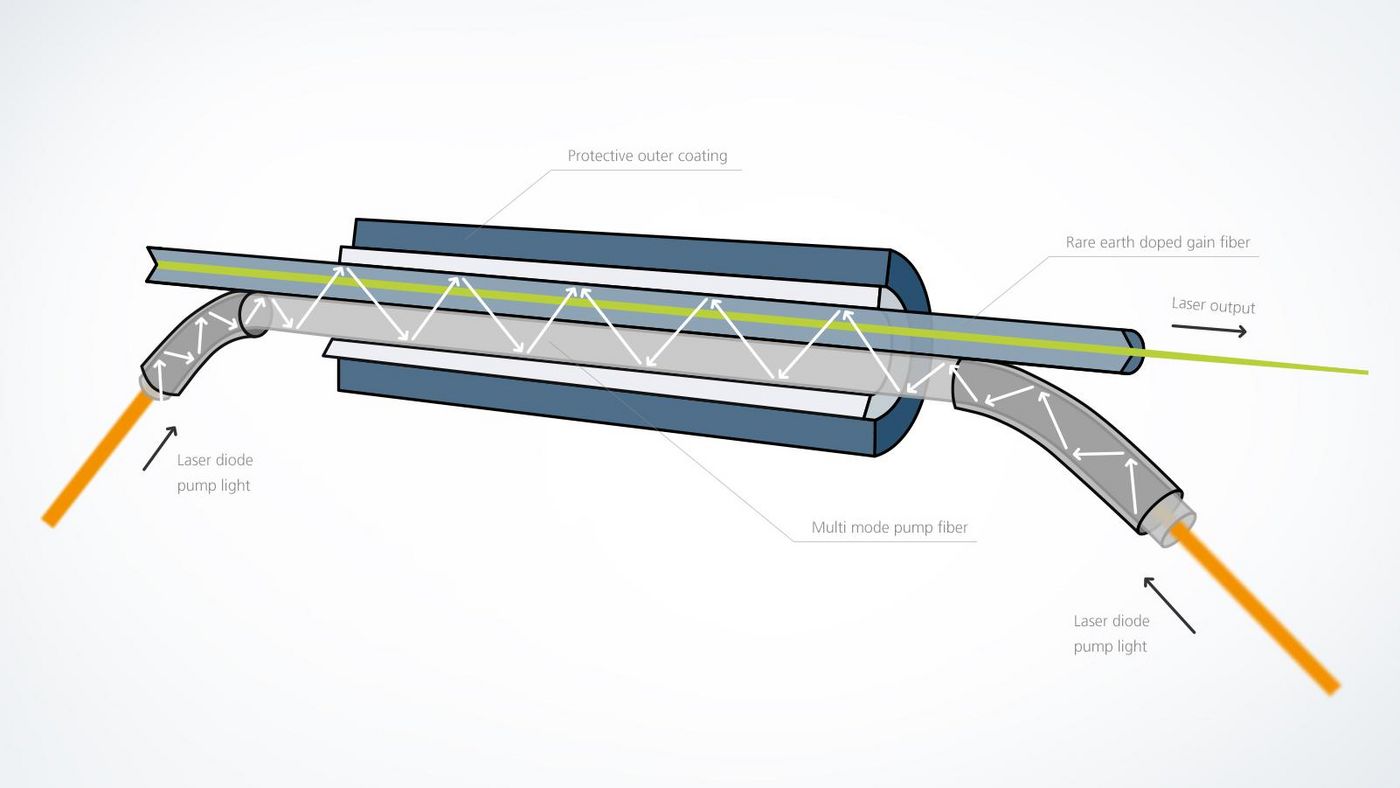
Okay, so lasers have three important parts: a beam source, a gain medium, and a resonator. The beam source uses power from outside to get the gain medium all excited. This excited state is called "population inversion," and it lets the medium make light bigger through a cool physical process called stimulated emission. Albert Einstein was the first to describe this (that's where LASER comes from - "Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation"). Inside the fiber, there are Fiber Bragg gratings that act like mirrors around the gain medium to make a resonator. This grabs the optical energy and makes it even bigger inside the resonator. Then, some of that energy comes out in one direction through a semi-transparent mirror, and that's the laser beam that we can use for all sorts of things. Fiber lasers are efficient and can control speed and power exactly right by managing things like beam length, how long it lasts, how intense it is, and how much heat it puts out.
Fiber Laser Cutting Advantages for Various Materials

Fiber lasers are like the pros when it comes to processing materials. They've been used in industry for years and are super reliable. They're especially popular for working with metals, and it doesn't really matter what kind of metal it is. They can manage mild steel, stainless steel, titanium, iron, nickel, and those shiny reflective metals like aluminum, brass, copper, and even precious metals like silver and gold. They also do an excellent job on materials with anodized or painted surfaces. And that's not all - pulsed nanosecond lasers (which are a type of fiber laser) can work on silicon, gemstones (even diamonds!), plastics, polymers, ceramics, composites, thin layers, bricks, and concrete.
How to Maximize Fiber Laser Cutting Advantages
So, MAX has diverse types of fiber lasers - pulsed, continuous wave (CW), and ultrashort pulse lasers. Pulsed fiber lasers send out laser beams in short bursts, and you can control how long each burst lasts, from nanoseconds to microseconds. CW lasers give a continuous beam, and they can also change the beam power up to the kHz frequency range. CW lasers are all about power and high output, so you'll find them a lot in industrial places. If you need high peak power in a short pulse, a pulsed fiber laser is the way to go. And then there are micro lasers with super short pulse durations - they can go down to 350 fs (femtoseconds)!
Applications That Highlight Fiber Laser Cutting Advantages
Laser Welding

This is when you join materials together, whether they're the same or different. Laser welding is all about quality and cost. You can weld all sorts of materials, from thick steel plates, fuel cells, and batteries to the tiny, delicate wiring in medical devices. It's like a welding wizard!
Laser Cutting
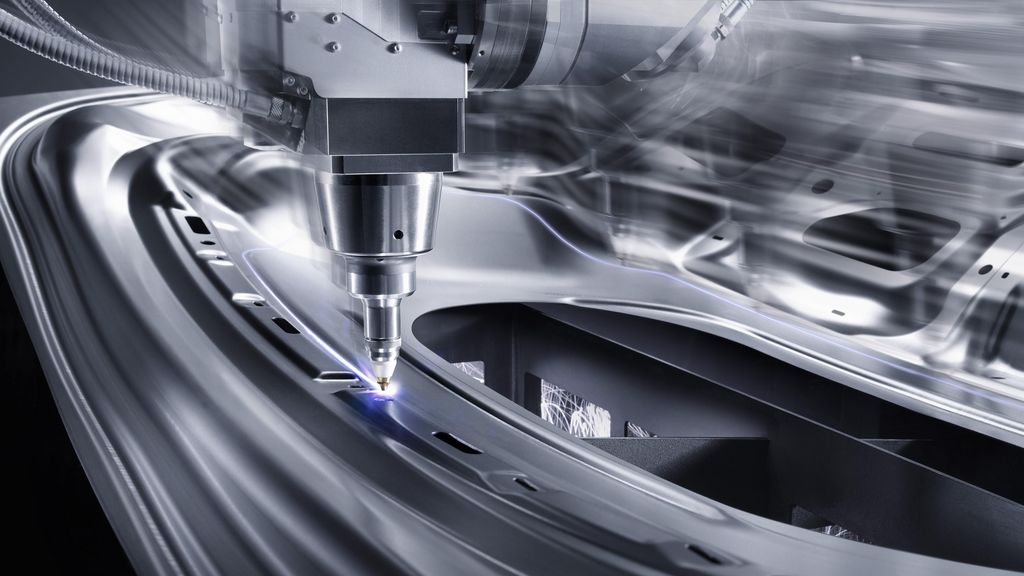

Here, you use a laser beam to cut through materials. It could be small, delicate stuff or thick things like sheet metal. The focused laser beam (pulsed or continuous wave) cuts into a wide range of materials with amazing precision. It's like a super precise cutting tool!
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)

This is the cool process of building a 3D part by adding material layer by layer. By using 3D printers and computer software, you can create all kinds of complex shapes. Fiber lasers are often the ones that supply the beam in these 3D printing systems. It's like building something from nothing, one layer at a time!
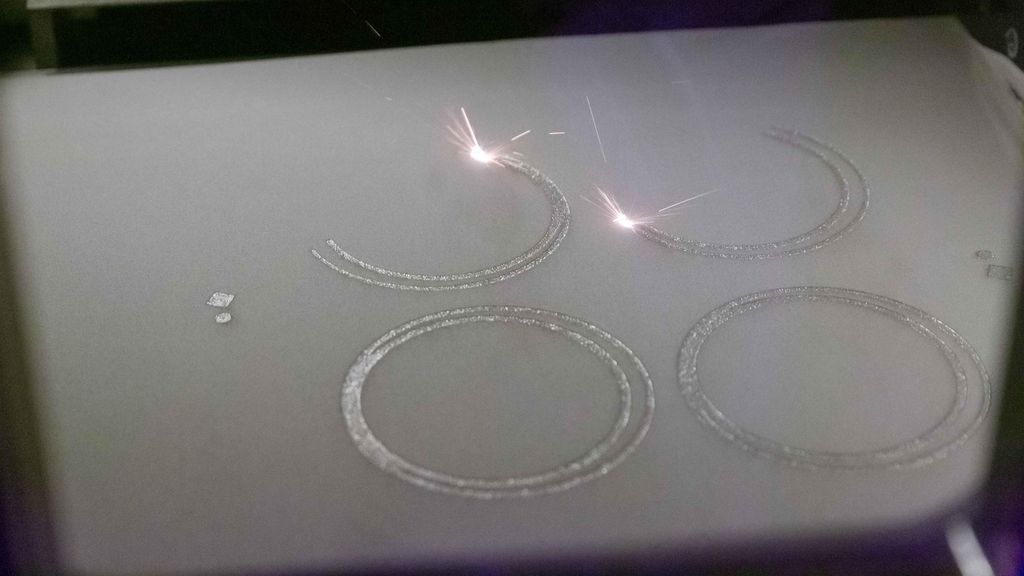
Laser Ablation

This is when you remove layers of material with a laser, precisely. You can take away all kinds of materials, from solid metals to ceramics to industrial compounds. It's used a lot in making electronics like semiconductors and microprocessors. The best part? It's super precise and you can do it in one step, which is way better than old-school methods like etching that need lots of steps. And it's more cost-effective and better for the environment too, since you don't need solvents or chemicals.
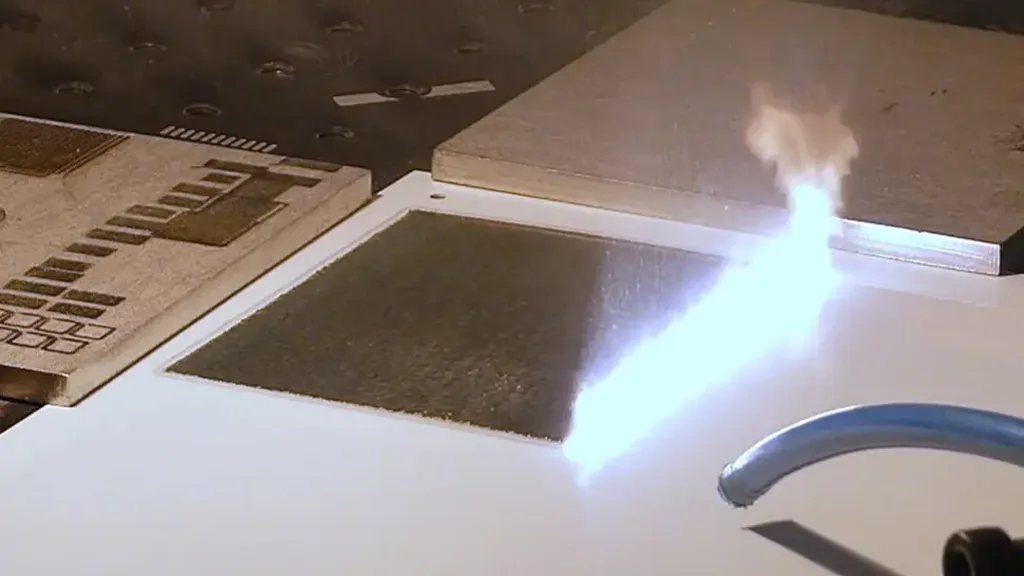
Laser Cleaning

This is all about getting rid of impurities, deposits, or contaminants from material surfaces using a laser. There are two types - one that takes off a single layer and one that removes the whole top layer. It's like giving your materials a clean sweep!
Laser Drilling
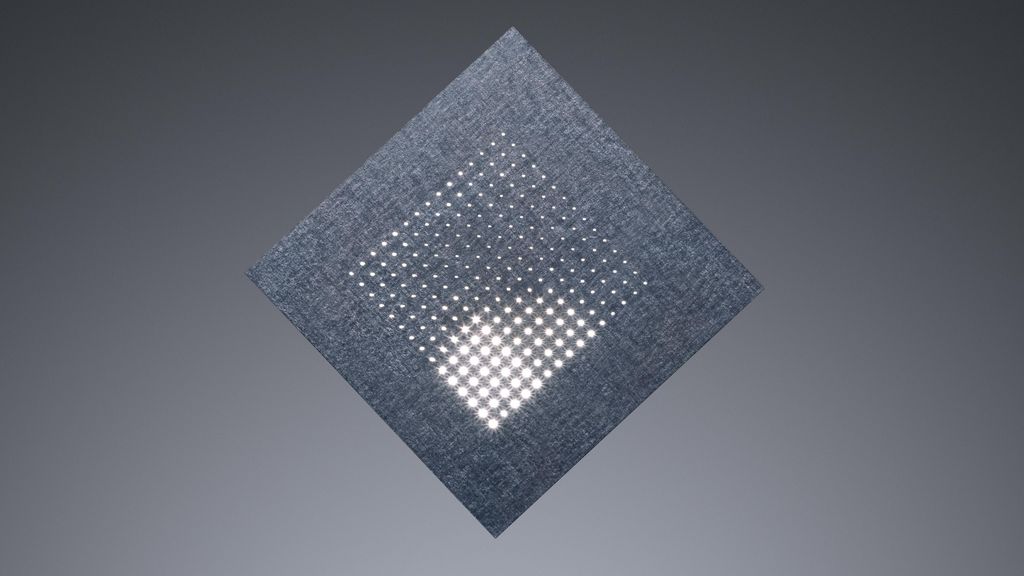
This is a cool non-contact way to make holes in materials. You keep pulsing the laser beam on a spot until the material vaporizes and melts, making a hole. It works differently depending on how thick the material is, how many holes you need, and how big they are. And the benefits? No contact means no wear or contamination, it's super repeatable, works with lots of materials, makes precise holes in all shapes and sizes, is easy to add to your production process, and you can set it up fast with fewer tools.
Laser Marking

Here, you use a strong, pulsed laser beam to put a mark right on the surface. When the laser hits the part surface, it changes the material and makes a visible mark - could be a discoloration, some structure, or just a mark. You can do this on all kinds of materials - metals, ceramics, plastics, LEDs, rubber, graphic composites, you name it!
Laser Engraving
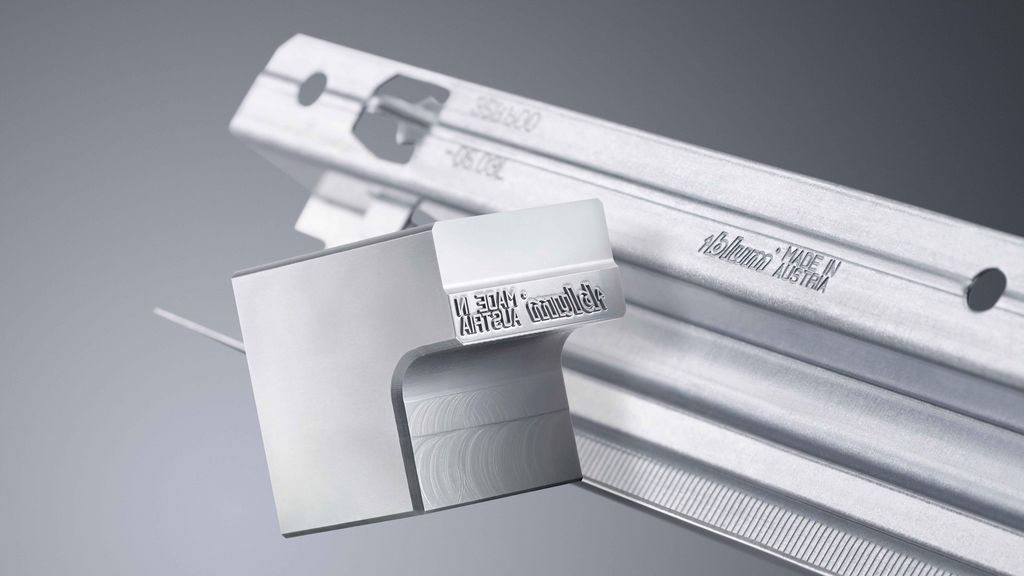

This is when you remove part of a material to leave an engraved mark. The laser acts like a chisel, blasting away parts of the material to make a mark that's under the surface. How deep the mark is depending on things like how long the laser stays on a spot, the energy of the pulse, how many times it passes over, and what kind of material it is.
Fiber Lasers vs. CO2 Lasers
Let's talk about the differences between fiber and CO2 lasers. Fiber lasers are the new kids on the block in the laser world. They don't have any moving parts or mirrors, which means super low maintenance costs. They're also really good with electricity and can work well with both thin and thick reflective metals. On the other hand, CO2 lasers are great for processing non-metallic materials like plastics, textiles, glass, acrylic, wood, and especially stone. They're better for thicker materials (usually over 5 mm thick) and can cut in a straight line faster than fiber lasers.
So, there you have it - the amazing world of MAX fiber lasers! Whether you're in manufacturing or just curious about how things are made, fiber lasers are definitely something to get excited about.
Summary
In this article, we have delved into MAX fiber lasers, covering their numerous benefits, working principles, applicable materials, diverse types, and typical applications, as well as comparing them with CO₂ lasers.
MAX fiber lasers prove wide versatility across various industries, being used in aerospace, automotive, medical, and many other fields. Their compact design saves space and can adapt to different installation environments. In terms of material processing, they can manage a vast range of materials, from common metals to various non-metallic materials. They are highly cost-effective, with a decent price/performance ratio and extremely minimal maintenance costs. They are also easy to integrate with existing systems and are energy efficient.
About the working principle, they generate a laser beam through the coordinated action of the beam source, gain medium, and resonator, and can precisely control speed and power.
For different manufacturing tasks such as laser welding, cutting, additive manufacturing, ablation, cleaning, drilling, marking, and engraving, MAX fiber lasers offer unique advantages and solutions, making them a valuable tool in modern manufacturing. Whether it is for high-power industrial applications like CW lasers in drilling and welding, or for precision tasks requiring highly specialized cuts with pulsed fiber lasers, they have proven their worth. Their ability to work with a wide variety of materials and provide precise and efficient processing makes them stand out in the manufacturing world. Overall, MAX fiber lasers are a remarkable technology that brings many benefits and possibilities to the manufacturing industry.