Laser welding machines have revolutionized the way metal is joined in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. Unlike traditional welding methods, a welding laser machine uses concentrated light energy to create precise and clean welds, offering unmatched accuracy and efficiency. For beginners looking to understand how these machines work and their advantages, this guide covers everything from basic principles to the types of materials that can be welded. Whether you're setting up your workshop or exploring laser welding for industrial purposes, this comprehensive guide will provide the foundation you need to get started.
Introduction to Laser Welding Technology
What is a Welding Laser Machine?
A welding laser machine is a specialized tool that uses focused laser beams to join materials, primarily metals, through a process called laser welding. This technology harnesses the intense energy of lasers to create high-quality welds with precision and speed. Welding laser machines can vary in design, from handheld devices to large industrial systems, making them suitable for various applications in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and more.
Overview of How Laser Welding Works
The process of laser welding involves directing a concentrated beam of light onto the material to be welded. When the laser beam strikes the surface, it generates heat, melting the material at the joint. As the molten metal cools, it solidifies, forming a strong bond between the pieces being joined. The process can be adjusted for different materials and thicknesses by altering the laser power, speed, and focus. Advanced systems may also incorporate automated controls and real-time monitoring to enhance precision and repeatability.
Advantages Over Traditional Welding Methods
Laser welding offers several advantages compared to traditional welding techniques:
- Precision: The focused nature of the laser allows for extremely accurate welds, minimizing the risk of errors and ensuring high-quality results.
- Speed: Laser welding can significantly reduce processing times, as the focused beam quickly melts and joins materials, making it ideal for high-volume production.
- Reduced Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): The concentrated heat minimizes the HAZ, leading to less distortion and improved mechanical properties of the welded materials.
- Versatility: Laser welding can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals and some plastics, expanding its applicability across different industries.
- Automation Compatibility: Many laser welding systems can be easily integrated into automated production lines, enhancing efficiency and consistency in manufacturing processes.
By leveraging these advantages, welding laser machines are becoming increasingly popular in modern fabrication and manufacturing settings, providing solutions that meet the demands of precision and speed.
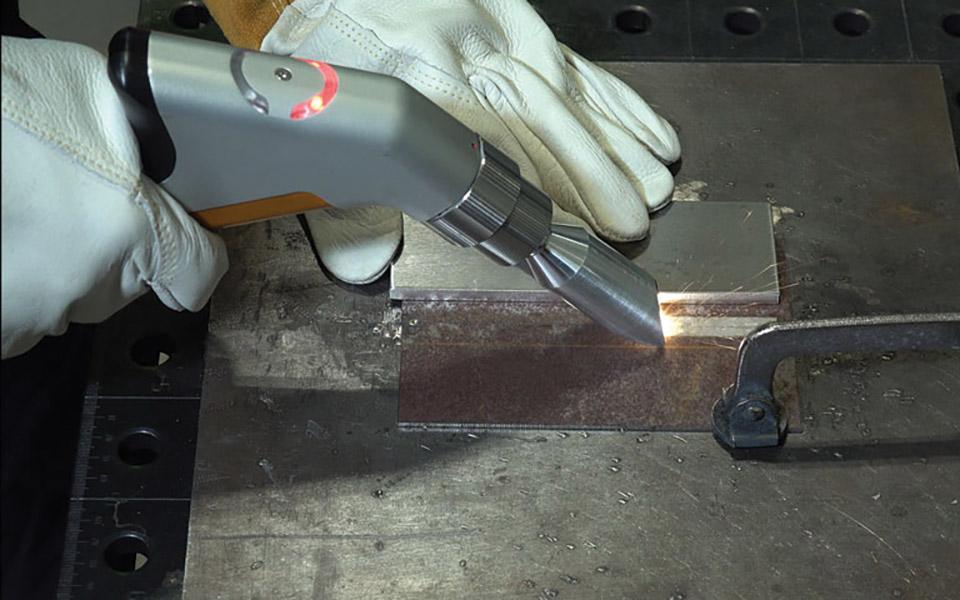
Components of Laser Welding Machine
Every handheld laser welder contain the following the component:
· Laser source
The laser source is the most important component of a handheld laser welding machine, and it directly affects the machine’s final weld area and life span. The most common sources are a solid-state laser and a fiber laser delivery such as HeatSign handheld laser welder. Both emit high-power laser beams and can weld thicker materials. They are more compact and provide higher welding speeds.
· Optical Cavity
The optical cavity surrounds the laser source. It consists of two reflective mirrors placed above and below the gain medium. The mirror surfaces serve as an amplifying system for the laser beam. As the laser beam bounces back and forth, they increase the length of the gain medium.
Furthermore, the degree of reflectivity varies between both mirrors. The first mirror reflects all light into the laser cavity. However, the mirror on the opposite side permits a small beam to exit the cavity to interact with the material.
· Cooling System
Laser welding is heat intensive. If heat is not removed or appropriately dissipated, it deforms thin materials. As a result, a cooling system is a critical part of the machine.
Experts use two main types of cooling systems when welding: liquid cooling and air cooling. Liquid cooling uses coolants, including water and other coolant fluids, which are transported directly to the parts generating heat. This provides a more efficient cooling medium.
· Power Supply
The electrical system provides the power that runs a handheld laser welding machine. The electrical current gets transformed into laser light that interacts with the materials. Controlling and monitoring the power density is important during welding as any change (even minute) can irreversibly damage the laser optics.
Furthermore, some handheld laser welding machines can be battery-operated. The battery type may vary based on the design of the welding equipment.
· Protective Housing
The laser welding machines must have protective housing to guarantee the operator’s safety. It ensures that the laser radiation in contact with the operator is within the MPE level.
Additionally, protective housing combines shielding windows, physical barriers, ventilation, and safety interlocks. They adequately contain the welding area and laser beam delivery system while granting the welder access to the entire welding operation.
· Welding Head
The welding head is responsible for delivering a highly concentrated laser beam to the welding joint for welding to take place. It comprises a focusing lens, shielding gas, and a protective nozzle which should come from highly durable material. It is also possible to adjust the machine parameters laser welding head to control heat input and distribution during the welding.
· Gas Supply System
The gas supply system ensures a smooth run of this heat-conduction welding process. This system provides gas, including helium and argon, that protects the welding area from unintended reactions with atmospheric content. When the atmospheric mixture reacts with the molten material, nitrogen embrittlement and oxidation can occur. The gasses also prevent weld contamination by removing impurities from the material surface.
How To Set Up and Install a Handheld Laser Welding Machine
There are four steps to set up and install a handheld laser welder, as highlighted below:
Step 1: Preparing the Workplace
In this step, you ensure that the environment where you will work with the handheld laser welding machine is set up
- Choose a well-ventilated area with controlled temperature and humidity levels.
- Clean all dirt and debris, as they can cause damage to the laser system.
- Ensure that the appropriate PPEs are available to prevent accidental exposure to laser radiation.
Step 2: Position the Machine and Install the Software
After successfully purchasing a handheld laser welding machine,
- Carefully unpack the machine and check for any loose or damaged components.
- If the machine is in order, place it on a level surface.
- Integrate the cooling and gas supply system based on the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Switch on the machine
- Install the software.
Step 3: Test Run the Machine
Finally, test runs the machine to check how it works. To do this,
- Calibrate the machine and adjust the laser parameters
- Following the instructions in the manual, create a simple weld joint with waste materials.
- Inspect the weld quality is up to standard.
Note: Ensure you train new laser welders for safety purposes and to improve performance
Advantages of Handheld Laser Beam Welding Machines
The introduction of handheld laser welding machines has brought about a remarkable change in manufacturing industries. The following are some advantages of using a handheld laser welding system for your applications.
· Portability and Versatility
This machine is compact and lightweight. They are ideal for heavy equipment and hard-to-reach parts that may be difficult for heavy welding machines. Furthermore, the size of the machine does not limit its capability. Because of their weight, they are suitable for a variety of applications. They are a valuable tool for manufacturing and repairing operations.
· Efficiency
The technologies and software that come with handheld laser marking systems are advanced. When comparing the machine to the MIG welding machine, there is higher production efficiency, precision, speed, and cost efficiency. Furthermore, handheld laser welders do not generate much waste.
These portable devices consume relatively low energy. This is an additional means to reduce a company’s operating costs while contributing to environmental sustainability.
· Small Heat-Affected Zone
They have a small heat-affected zone, which ensures that the welded joint is as accurate and has little heat impact on areas adjacent to the welding joint. The laser beam of a handheld welding machine is adequately focused on the material joint, which limits the amount of heat that gets transferred. This property makes them applicable for use in the manufacturing industries. They are the go-to machine to weld small and delicate pieces that are heat sensitive.
· User-friendly
The machines have an intuitive user interface, making them easier for people of different technical minds. With a single button push, the laser welder can adjust the laser parameters to suit your project needs. This reduces the chance of occupational hazards and promotes operator satisfaction.
Types of Welding Laser Machines
Handheld Welding Laser Machines
Handheld welding laser machines are compact, versatile tools designed for ease of use in various applications. These machines allow operators to perform laser welding with a high degree of control, making them ideal for smaller projects, repairs, or intricate welds in hard-to-reach areas. They are typically lightweight and can be maneuvered easily, offering flexibility for onsite work. Handheld machines are popular in industries such as automotive repair, metal fabrication, and construction, where quick and precise welding is essential.
Automated Welding Laser Machines
Automated welding laser machines are designed for high-volume production and precision welding tasks. These systems often integrate robotics and advanced control technology, allowing for consistent, repeatable welds with minimal human intervention. Automated machines are commonly used in manufacturing environments, such as automotive assembly lines, where speed and accuracy are critical. They can be programmed to execute complex welding patterns and can handle larger workpieces compared to handheld machines, making them suitable for mass production.
Portable vs. Industrial-Grade Machines
When considering welding laser machines, it's important to differentiate between portable and industrial-grade models:
- Portable Machines: These are lightweight, easy to transport, and typically have a lower power output. They are designed for use in various settings, including workshops, construction sites, and field operations. Portable machines are ideal for smaller projects, maintenance work, and applications where flexibility is needed.
- Industrial-Grade Machines: Industrial-grade welding laser machines are robust, high-performance systems built for heavy-duty use in manufacturing environments. They offer higher power levels, larger working areas, and advanced features for automation. These machines are designed for high-volume production and are often equipped with sophisticated monitoring and control systems to ensure consistent quality and efficiency.
By understanding the different types of welding laser machines available, users can select the right equipment based on their specific needs, whether for small-scale operations or large industrial applications.
Materials Suitable for Laser Welding
Metals Commonly Welded
Laser welding is highly effective for a variety of metals, including:
- Steel: Both carbon and stainless steels are widely welded using laser technology due to their excellent weldability and strength. Laser welding is particularly advantageous for thin sections of steel, as it minimizes distortion and maintains structural integrity.
- Aluminum: Laser welding of aluminum is beneficial for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. However, it requires specific parameters to address its thermal conductivity and reflective nature, making it suitable for automotive and aerospace applications.
- Titanium: Known for its strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, titanium is often welded with lasers in industries such as aerospace and medical. Laser welding helps achieve high-quality joints without compromising material properties.
Special Materials and Alloys
Certain special materials and alloys also benefit significantly from laser welding:
- Copper Alloys: Laser welding can effectively join copper and its alloys, which are challenging to weld using traditional methods due to their high thermal conductivity. The precision of laser welding helps create strong joints while minimizing heat input.
- High-Performance Alloys: Alloys used in aerospace and military applications, such as Inconel and Monel, can be welded with lasers, providing strong joints and excellent performance under extreme conditions.
- Composite Materials: Some advanced composite materials can also be laser welded, allowing for the integration of metal components in lightweight structures.
Limitations and Considerations for Different Materials
While laser welding is versatile, there are limitations and considerations to keep in mind:
- Reflective Materials: Materials with high reflectivity, such as copper and brass, can pose challenges as they reflect laser energy. Special techniques, like using longer wavelengths, may be required.
- Thickness: The effectiveness of laser welding can vary with the thickness of the material. Thicker materials may require higher power levels or additional processing methods to achieve good penetration and quality.
- Thermal Sensitivity: Some materials may be sensitive to heat, leading to warping or changes in properties. Proper parameter settings and techniques are crucial to mitigate these issues.
- Material Composition: The presence of impurities or variations in alloy composition can affect weld quality. Ensuring material consistency and proper surface preparation is essential for successful laser welding.
Understanding these materials and their specific requirements helps in selecting the right approach and optimizing the laser welding process for various applications.
Applications of Laser Welding
Industries That Benefit from Laser Welding
Laser welding is utilized across various industries due to its precision, speed, and versatility. Key industries include:
- Automotive: Laser welding is extensively used in automotive manufacturing for assembling body parts, chassis components, and fuel tanks. The technology allows for lightweight constructions and high-strength joints, improving vehicle performance and safety.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace sector, laser welding is crucial for joining high-performance materials such as titanium and aluminum. It ensures strong, lightweight assemblies that can withstand extreme conditions, making it ideal for components like aircraft frames and engine parts.
- Electronics: The electronics industry employs laser welding for assembling delicate components, such as circuit boards and battery packs. The precision of laser welding minimizes thermal distortion and ensures reliable connections in compact designs.
- Medical Devices: Laser welding is widely used in manufacturing medical devices, including surgical instruments and implants. The clean and precise welds meet stringent hygiene and performance standards, essential for medical applications.
- Manufacturing: Various manufacturing sectors utilize laser welding for fabricating parts in appliances, machinery, and consumer goods. Its ability to create strong joints quickly enhances productivity and product quality.
Common Use Cases and Real-World Examples
Laser welding has numerous practical applications, including:
- Automotive Body Welding: Major automotive manufacturers like Ford and BMW use laser welding to assemble vehicle bodies, ensuring high-strength connections while reducing weight.
- Aerospace Component Assembly: Companies such as Boeing and Airbus rely on laser welding to join aluminum and titanium components in aircraft fuselages and wings, optimizing performance and safety.
- Electronic Device Assembly: Manufacturers like Apple and Samsung use laser welding for assembling batteries and circuit boards in smartphones and tablets, ensuring compact designs and reliable performance.
- Medical Implant Production: Companies that produce orthopedic implants utilize laser welding to create strong, biocompatible joints that meet rigorous safety and performance standards.
- HVAC Systems: Laser welding is used to assemble components in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, providing durable and leak-proof connections.
These applications illustrate how laser welding technology has become integral to modern manufacturing processes, offering solutions that enhance product quality and production efficiency across diverse industries.
Tips for Beginners
How to Choose the Right Machine Based on Your Needs
When selecting a handheld laser welding machine, consider the following factors:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine can weld the specific materials you'll be working with, such as steel, aluminum, or titanium. Check the machine's specifications for power output and settings suitable for those materials.
- Power Requirements: Assess your welding tasks to determine the required power level. Higher wattage machines are better for thicker materials, while lower wattage units are suitable for thin sheets.
- Portability and Size: If you plan to work in various locations, opt for a lightweight and portable machine. Consider the size of the work area and the complexity of your projects.
- User-Friendliness: Look for machines with intuitive controls and clear instructions. Features like adjustable settings and automatic focusing can simplify the welding process for beginners.
- Budget: Determine your budget and find a machine that offers the best balance of features and performance within your price range. Don't forget to factor in potential costs for accessories and maintenance.
Starting with Small Projects and Progressing to Advanced Tasks
Begin your laser welding journey with small, manageable projects. This approach allows you to gain confidence and develop your skills without feeling overwhelmed. Start with simple tasks, such as joining scrap pieces of metal, and gradually progress to more complex projects, like fabricating components for specific applications. As you build your experience, you can experiment with different materials and techniques, enhancing your proficiency and versatility.
Resources for Further Learning and Skill Development
To further your knowledge and skills in laser welding, consider exploring the following resources:
- Online Courses and Webinars: Many platforms offer courses focused on laser welding techniques, safety practices, and machine operation. Look for webinars hosted by industry experts for up-to-date information.
- YouTube Tutorials: Numerous channels provide instructional videos on laser welding basics, tips, and troubleshooting. Visual demonstrations can be incredibly helpful for beginners.
- Books and Manuals: Invest in books that cover laser welding principles, techniques, and best practices. Manufacturer manuals can also provide valuable insights into specific machines.
- Forums and Community Groups: Join online forums or social media groups dedicated to welding. Engaging with experienced welders can offer valuable advice, troubleshooting tips, and encouragement.
By following these tips, beginners can effectively navigate the world of laser welding, ensuring a successful and rewarding experience.
Conclusion
Choosing the right handheld laser welding machine is crucial for the overall success of the welding process. By considering the factors mentioned above, you can enhance welding quality and increase productivity. If you have any questions about handheld laser welding machines, feel free to reach out to us or explore the KRRASS Handheld Laser Welder, which offers exceptional quality and performance.






Reviewed by 1 user
TRAINER
WHAT IS THE MAXIMUM THICKNESS TO BE WELDED USING THIS EQUIPMENT