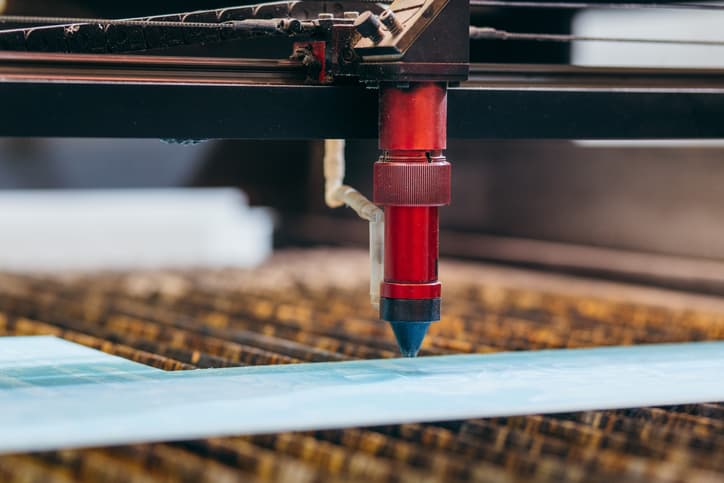
In the current processing industry, laser cutting machines have become a staple for various applications. Their efficiency and flexibility address challenges posed by traditional CNC punch machines. Laser cutting machines offer a non-contact processing solution, showcasing remarkable features such as minimal mechanical stress and deformation, straightforward operation, high cutting accuracy, and a small heat-affected zone.
Laser cutting stands out as the paramount application technology in the laser processing industry, constituting over 70% of the entire sector. Globally recognized as the most advanced cutting technology, laser cutting boasts precision manufacturing, flexible cutting, specialized shaping, one-time molding, high-speed operations, and unparalleled efficiency. It effectively tackles industrial production challenges that conventional methods struggle to resolve. Laser technology enables the cutting of a wide range of metallic and non-metallic materials.
1.What is Laser Cutting
Laser cutting, a revolutionary technology in the realm of manufacturing, harnesses the power of high-energy density laser beams to achieve precision and efficiency in cutting various materials. The process involves heating the workpiece with a concentrated laser beam, rapidly elevating the temperature to the material's boiling point within an extremely short timeframe. As a result, the material vaporizes, creating a clean and precise cut.
Materials such as stainless steel with a thickness below 4mm find efficient application in laser cutting devices. For thicker materials like 20mm carbon steel, laser cutting with oxygen assistance is employed, albeit with the side effect of forming a thin oxide layer on the cut surface.
One notable advantage of laser cutting is the absence of tooling costs. This makes laser cutting equipment suitable for the production of small-batch components of various sizes that were previously challenging to process using traditional methods.
Typically equipped with Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems, laser cutting devices receive cutting data from Computer-Aided Design (CAD) workstations through telecommunication lines.
The fundamental principle of laser cutting involves the focused, high-power density laser beam illuminating the workpiece, causing rapid melting, vaporization, ablation, or reaching the ignition point of the material. Simultaneously, a high-speed airflow, coaxial with the beam, blows away the melted material, facilitating the cutting process. Laser cutting stands as one of the thermal cutting methods.

2.Advantages of Ultra-Efficient Laser Cutting
A. Increased Precision
One of the standout advantages of ultra-efficient laser cutting lies in its ability to deliver unparalleled precision. As the laser beam is meticulously controlled through Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems, it ensures that cuts are made with microscopic accuracy. This precision is especially crucial in industries where intricate designs and tight tolerances are non-negotiable.
B. Enhanced Speed and Throughput
Ultra-efficient laser cutting is synonymous with remarkable speed and throughput. The process of laser cutting allows for swift and seamless material processing, significantly reducing production time. This increased efficiency translates into higher throughput, making it an ideal choice for manufacturers aiming to optimize their production workflows without compromising on quality.
C. Material Versatility
The versatility of ultra-efficient laser cutting is a game-changer in the manufacturing landscape. Laser cutting can be categorized into four types: laser vaporization cutting, laser melting and cutting, laser oxygen cutting, and laser marking and control fracture.
1. Laser Vaporization Cutting: This method involves rapidly heating the workpiece with a high-energy-density laser beam, causing the material to vaporize. Laser vaporization cutting is ideal for extremely thin metals and non-metals like paper, fabric, wood, plastic, and rubber.
2. Laser Melting and Cutting: In this approach, the laser heats the metal material to melting point, and a non-oxidizing gas is ejected through a coaxial nozzle, expelling the liquid metal under strong pressure to form the cut. It is particularly useful for cutting materials resistant to oxidation, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and their alloys.
3. Laser Oxygen Cutting: Similar to oxy-fuel cutting, laser oxygen cutting employs laser as the preheating heat source and reactive gases like oxygen for cutting. This method is efficient for easily oxidizable metals like carbon steel, titanium steel, and heat-treated steel, offering faster cutting speeds compared to vaporization and melting cutting.
4. Laser Marking and Control Fracture: Laser marking involves scanning the surface of brittle materials with a high-energy-density laser, creating small grooves. Applied pressure then induces controlled fractures along these grooves. This technique is often used for materials like glass.
3.Types of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting technology encompasses various methods, each tailored to specific materials and applications. Here are the primary types of laser cutting techniques:
1. Laser Vaporization Cutting
In laser vaporization cutting, a high-energy-density laser beam rapidly heats the workpiece, elevating the temperature to the material's boiling point in an extremely short timeframe. This process results in the formation of vapor, which forcefully exits the material, creating a cut. Laser vaporization cutting is particularly effective for thin metals and non-metals such as paper, fabric, wood, plastic, and rubber. Due to the substantial heat of vaporization, this method requires significant power and power density.
2. Laser Melting and Cutting
In laser melting and cutting, the laser heats the metal material to the point of melting. Subsequently, a non-oxidizing gas (e.g., Ar, He, N) is jetted through a coaxial nozzle, expelling the liquid metal under pressure to create the cut. This method is advantageous as it doesn't require complete vaporization of the metal, reducing the energy needed to one-tenth of that in vaporization cutting. Laser melting and cutting find applications in materials resistant to oxidation, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and their alloys.
3. Laser Oxygen Cutting
Similar to oxy-fuel cutting, laser oxygen cutting uses laser as the preheating heat source and reactive gases like oxygen for cutting. The process involves a reaction between the incoming gas and the metal, causing oxidation and releasing a substantial amount of heat. Simultaneously, molten oxides and metal are blown out of the reaction zone, forming a cut in the metal. Laser oxygen cutting requires only half the energy compared to melting cutting, resulting in significantly faster cutting speeds. This method is suitable for easily oxidizable metals like carbon steel, titanium steel, and heat-treated steel.

4. Laser Marking and Control Fracture
Lastly, laser cutting includes the techniques of laser marking and control fracture. Laser marking involves using a high-energy-density laser to scan the surface of brittle materials, creating small grooves. Applying pressure then induces controlled fractures along these grooves. This method is often employed for materials like glass. Fracture control utilizes the steep temperature distribution produced by laser engraving to induce local thermal stress in brittle materials, causing them to fracture along predefined paths.
4.Applications Across Industries
A. Automotive Sector
The automotive sector stands as a testament to the transformative impact of ultra-efficient laser cutting technology. In this industry, precision is paramount, and laser cutting ensures the production of intricate components with razor-sharp accuracy. From cutting complex shapes in body panels to crafting precision parts for engines, laser cutting has become indispensable. The speed and versatility of laser cutting also contribute to streamlined production processes, enhancing overall efficiency in the manufacturing of automobiles.
B. Aerospace Innovations
The aerospace industry, characterized by its demand for lightweight and high-strength materials, has found a reliable ally in ultra-efficient laser cutting. Laser cutting enables the fabrication of intricate components for aircraft, spacecraft, and satellites with unmatched precision. Whether it's shaping fuselage components or crafting intricate designs for aerostructures, laser cutting technology plays a pivotal role. The ability to cut through a variety of materials, including alloys used in aerospace applications, makes laser cutting a cornerstone of innovation in this demanding industry.
C. Electronics Manufacturing
In the fast-paced world of electronics manufacturing, where miniaturization and precision are key, ultra-efficient laser cutting technology has become a driving force. Laser cutting is employed in the production of circuit boards, ensuring precise and clean cuts for intricate designs. The flexibility of laser cutting machines allows for the creation of custom shapes and patterns, catering to the ever-evolving demands of electronic components. From smartphones to advanced electronic systems, laser cutting contributes to the production of compact and efficient electronic devices that power our modern world.
5.Key Components of Laser Cutting Systems
A. High-Precision Lasers
The cornerstone of any effective laser cutting system is the deployment of high-precision lasers. These lasers, often solid-state or fiber lasers, emit a concentrated beam of light with incredible accuracy. The choice of laser type depends on the specific requirements of the application. Solid-state lasers, for example, are known for their robustness and suitability for heavy-duty industrial applications, while fiber lasers excel in delivering high beam quality, crucial for intricate and precise cutting tasks. The ability to generate a focused and intense beam is fundamental to achieving the precision demanded by various industries.
B. Advanced Optics
Another vital component in laser cutting systems is the integration of advanced optics. These optics play a pivotal role in shaping and focusing the laser beam to achieve the desired cutting results. High-quality lenses and mirrors ensure that the laser beam remains sharp and focused throughout the cutting process. Additionally, beam delivery systems, such as beam splitters and collimators, contribute to the efficiency and precision of the laser cutting system. The synergy between high-precision lasers and advanced optics is crucial for delivering intricate, clean, and accurate cuts across a range of materials.
C. Intelligent Control Systems
Intelligent control systems serve as the brains behind the brawn of laser cutting technology. These systems, often computerized and driven by sophisticated software, provide precise control over the movement of the laser cutting head and the manipulation of the laser beam. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology is frequently employed to execute complex cutting patterns with microscopic accuracy. The intelligence embedded in these control systems allows for the customization of cutting parameters, ensuring adaptability to various materials and thicknesses. The seamless coordination between high-precision lasers, advanced optics, and intelligent control systems is the key to unlocking the full potential of laser cutting technology.

6.How to Choose the Right Laser Cutting Machine
Investing in a laser cutting machine is a strategic decision that can significantly impact the efficiency and quality of your manufacturing processes. To ensure you make the right choice, consider the following factors when selecting a laser cutting machine:
1. Material Compatibility
Determine the types of materials you will be working with. Different laser cutting machines are optimized for specific materials, so it's crucial to choose a machine that can handle the materials relevant to your applications. Whether it's metals, plastics, or composites, ensure the machine is designed for the materials you intend to process.
2. Cutting Speed and Precision
Assess your production requirements in terms of cutting speed and precision. Laser cutting machines vary in their capabilities, so align your needs with the machine's specifications. Consider whether you prioritize faster production rates or require intricate detailing, and choose a machine that strikes the right balance for your specific applications.
3. Power and Wattage
The power and wattage of the laser cutting machine play a crucial role in its performance. Higher wattage machines generally offer greater cutting capabilities, allowing for thicker materials and faster cutting speeds. Evaluate the power requirements based on the thickness and type of materials you plan to process regularly.
4. Bed Size and Configuration
Consider the size of the cutting bed, as it determines the maximum dimensions of the materials you can work with. Additionally, assess the configuration of the bed, whether it's a fixed bed or a gantry-style bed. The bed size and configuration should align with the scale and nature of your manufacturing projects.
5. Automation and Software Compatibility
Look for features related to automation, as they can significantly enhance productivity. Automated loading and unloading systems, as well as compatibility with advanced software for design and cutting, contribute to seamless and efficient operations. Ensure the laser cutting machine integrates well with your existing workflow and software tools.
Conclusion
Unlock the potential of ultra-efficient laser cutting technology with our in-depth exploration. From understanding the types and applications to choosing the right machine, discover the key components that drive precision and innovation. Dive into the world of laser cutting and explore why Krrass stands out as China's premier Laser Cutting Machine manufacturer and solution provider. Visit their website at Krrass to elevate your manufacturing capabilities.