In the manufacturing industry, choosing the right equipment can significantly impact efficiency, productivity, and product quality. One crucial decision many businesses face is selecting the right press brake machine. With advancements in technology, the two most prominent types of press brakes available today are hydraulic and electric. Understanding the key differences between hydraulic vs electric press brake systems is essential for making an informed choice that aligns with your operational needs. This article delves into the unique characteristics, advantages, and considerations of hydraulic and electric press brakes, helping you determine which is best suited for your manufacturing requirements.
Development and Evolution of Press Brakes
The press brake has been a cornerstone of metal fabrication for decades, continually evolving to meet the growing demands of various industries. Initially, mechanical press brakes dominated the market, offering basic functionality with limited precision. As technology advanced, hydraulic press brakes emerged, revolutionizing the industry with their increased power and control.
Hydraulic press brakes use hydraulic cylinders to apply force, providing greater bending power and consistency. They became the standard in many fabrication shops due to their ability to handle thicker materials and deliver more precise bends. The introduction of computer numerical control (CNC) further enhanced their capabilities, allowing for automated, highly accurate operations.

In recent years, the advent of electric press brakes has marked another significant leap in the evolution of this essential machinery. Electric press brakes use servo-electric motors instead of hydraulic systems, offering unparalleled precision, energy efficiency, and lower maintenance requirements. They are particularly favored in industries where high accuracy and repeatability are critical.
The development of hybrid press brakes, which combine the strengths of both hydraulic and electric systems, represents the latest innovation in press brake technology. These machines offer the power and flexibility of hydraulic systems with the efficiency and precision of electric motors, providing a versatile solution for modern fabrication needs.
What Is Hydraulic Press Brake
A hydraulic press brake is a machine used in the metal fabrication industry to bend and shape metal sheets and plates. It operates using hydraulic cylinders that generate force through the movement of hydraulic fluid under pressure. This force is then applied to a punch and die set, which bends the metal into the desired shape.
Key Components of a Hydraulic Press Brake:
- Hydraulic System: The core of the machine, consisting of hydraulic cylinders, pumps, and fluid. The hydraulic system is responsible for generating the pressing force required to bend the metal.
- Frame: The robust structure that supports the machine and withstands the high pressures involved in the bending process.
- Punch and Die: Tools attached to the upper and lower beams of the press brake. The punch forces the metal into the die to create the bend.
- Back Gauge: A positioning tool that ensures the metal sheet is correctly aligned for precise bends. It can be manually adjusted or automated in CNC (computer numerical control) press brakes.
- Controller: Modern hydraulic press brakes often feature CNC controllers that automate the bending process, ensuring high precision and repeatability.
How Does Hydraulic Press Brake Work
Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system serves as the heart of the hydraulic press brake, comprising hydraulic pumps, control valves, cylinders, and oil tanks. Its primary function is to draw hydraulic oil from the reservoir and regulate pressure and flow through control valves to drive the cylinder piston for reciprocating motion. This motion of the piston in the cylinder controls the bending action of the upper and lower dies, shaping the metal sheet.
Cylinder and Piston Movement
In an electric press brake, the cylinder is typically driven directly by a motor, causing the piston to move up and down via motor transmission. In contrast, the hydraulic press brake regulates cylinder and piston movement through hydraulic power, ensuring more stable and precise motion control.
Hydraulic Power Transmission and Regulation
The hydraulic press brake employs hydraulic power transmission, offering notable benefits such as high stability and rapid response. This hydraulic system enables precise control over pressure and speed, making it well-suited for applications requiring high precision in workpiece bending.
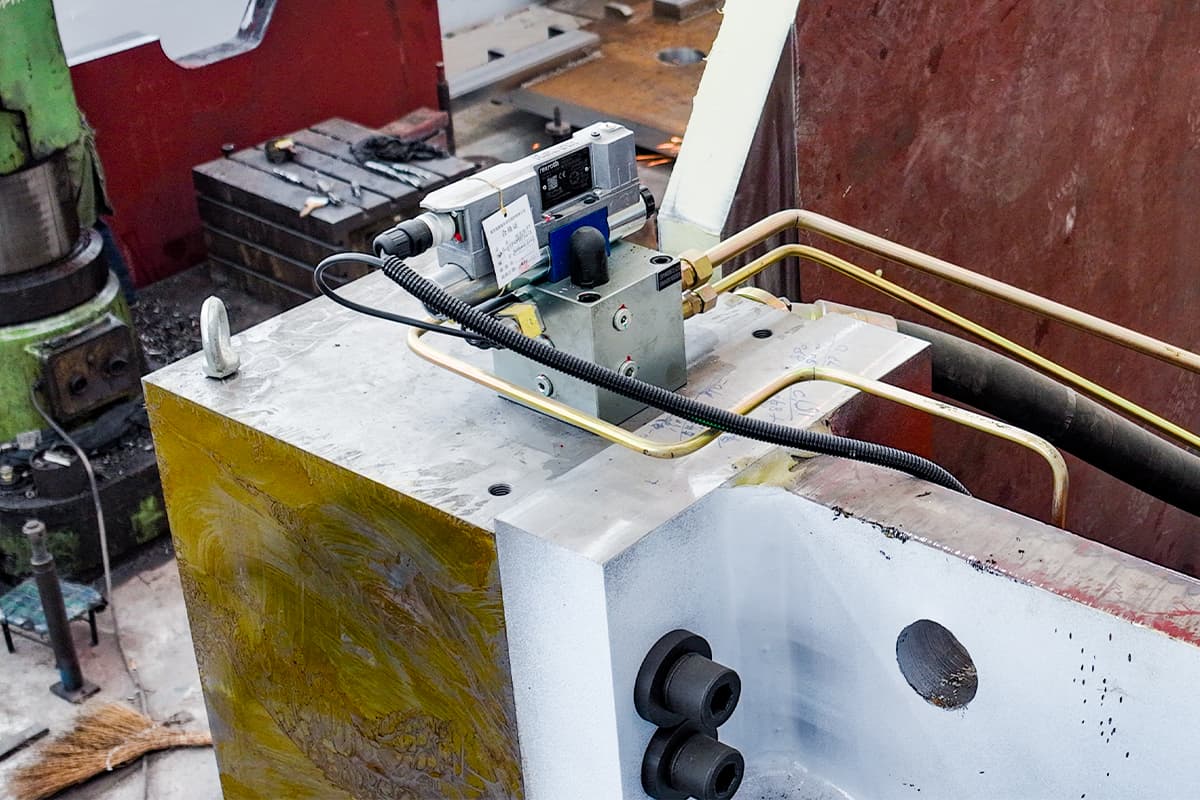

Pros of Hydraulic Press Brake
Hydraulic press brakes offer several advantages over their mechanical and electric counterparts, making them a popular choice in metal fabrication.
Enhanced Precision
Hydraulic press brakes excel in providing superior precision for bending operations. The machine's operator controls enable accurate manipulation of the ram’s motion, speed, and applied force, ensuring highly precise bend angles.
Improved Safety
Safety is another significant advantage of hydraulic press brakes. The integration of computer controls enhances operational control, thereby reducing the risk of errors. Additionally, most hydraulic press brakes are equipped with safety devices designed to prevent accidents and protect operators.
Versatility
One of the standout benefits of hydraulic press brakes is their versatility. They are capable of handling various metals, different tonnages, and a range of sheet thicknesses. Furthermore, these machines can form an array of shapes, making them suitable for a wide spectrum of industrial applications.
Cons of Hydraulic Press Brake
However, it is important to note that hydraulic press brakes also have some disadvantages. One of the biggest concerns is their high cost of ownership, as hydraulic systems tend to be more expensive to purchase, maintain and repair than electric systems. This type of press brake machine also requires a hydraulic power source, which can be expensive to set up and maintain.
- High Energy Consumption
- Maintenance Requirements
- Environmental Concerns
- Initial Cost
What Is Electric Press Brake
An electric press brake is a type of metalworking machine used to bend and shape metal sheets and plates using an electric servo motor system instead of the traditional hydraulic system. This technology offers precise, efficient, and environmentally friendly alternatives to hydraulic press brakes.
What are the Different Electric Press Brake Types
Servo-Electric Press Brake:
A servo-electric press brake is a subset of electric press brakes powered by servo motors. These machines enable high-speed bending operations by moving the ram through a ball screw or belt drive mechanism, converting rotary motion into linear motion for bending.
Features:
- Energy Efficiency: Servo motors consume electricity only during ram motion, reducing overall energy consumption.
- Cleaner Operation: Absence of hydraulics makes them environmentally friendly.
Electro-Hydraulic Press Brake:
Electro-hydraulic press brakes combine hydraulic systems with electric servo motors, offering the power of hydraulics with the precision of servo-electric systems.
Features:
- Precision: Offers higher accuracy and repeatability than traditional hydraulic press brakes.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric servo motors reduce idle energy consumption.
Hybrid Press Brake:
Hybrid press brakes blend hydraulic and electric technologies, using a small quantity of oil pressurized by electrically driven hydraulic pumps.
Features:
- Energy Efficiency: Decreased energy consumption while retaining hydraulic power.
- High Precision: Offers precision similar to all-electric models.
Direct Drive Electric Press Brake:
Direct drive electric press brakes feature a motor directly connected to the ram, eliminating the need for a pulley system.
Features:
- Energy Efficiency: Less energy loss compared to other types.
- Precision Control: Allows for precise bending and high accuracy.
Key Components of an Electric Press Brake:
- Electric Servo Motors: The core of the machine, these motors drive the ram's movement with high precision and control.
- Ball Screws or Belt Drives: These components convert the rotational motion of the servo motors into linear motion, enabling the ram to move up and down.
- Frame: A robust structure that supports the machine and withstands the forces generated during the bending process.
- Punch and Die: Tools attached to the upper and lower beams of the press brake. The punch forces the metal into the die to create the bend.
- Back Gauge: A positioning tool that ensures the metal sheet is correctly aligned for precise bends. It can be manually adjusted or automated in CNC (computer numerical control) press brakes.
- Controller: Advanced electric press brakes often feature CNC controllers that automate the bending process, ensuring high precision and repeatability.
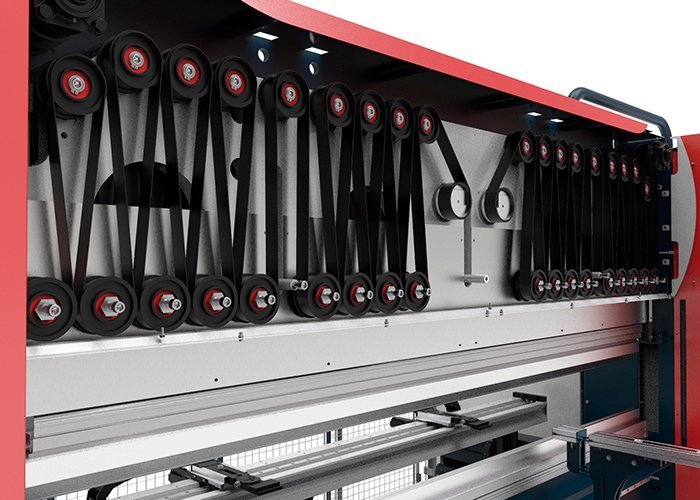

How Does Electric Press Brakes Work
Motor Drive:
The motor drive is a fundamental component of modern industrial automation, vital across various industries. It controls parameters such as speed, direction, and torque of the motor to achieve precise control of mechanical equipment. High-performance control algorithms and precise sensor feedback ensure stable motor operation in different working environments.
Transmission System:
The transmission system transfers power from the motor to the working mechanism of the press brake. In an electric press brake, it typically consists of gears, transmission rods, and connecting components. These parts are precisely designed for efficient and stable power transmission. Gears engage and transmission rods rotate to transfer power to the upper and lower dies, enabling them to bend the metal sheet. Optimal design improves bending accuracy and efficiency.
Motion of Working Components:
The working components of an electric press brake include the upper and lower dies and the press beam. Driven by the motor, the transmission system moves these components to bend the metal sheet. Motion can be linear or curvilinear, depending on processing requirements. Linear motion suits simple bending, while curvilinear motion achieves complex shapes. Various dies and press beams accommodate different sheet sizes and shapes for diverse processing needs.
Pros of Electric Press Brake
Energy Efficiency: Electric press brakes consume less energy than hydraulic models, resulting in cost savings and a smaller environmental impact.
Precision: Electric press brakes feature advanced control systems that offer superior precision and repeatability, essential for high-quality metal fabrication.
Speed: Electric press brakes are recognized for their high operating speed, which enhances productivity levels.
Reduced Maintenance: Unlike hydraulic press brakes, electric models eliminate the need for regular oil changes, leading to decreased maintenance costs.
Noise Reduction: Electric press brakes operate with lower noise levels, improving the overall working environment.
Cons of Electric Press Brakes
Higher Initial Cost: Electric press brakes generally have a higher initial purchase cost compared to hydraulic models, which may pose a financial challenge for some buyers.
Limited Tonnage: Electric press brakes may have limitations in terms of tonnage compared to hydraulic press brakes, which can restrict their suitability for certain heavy-duty applications.
Complexity: Electric press brakes can be more complex to operate and maintain compared to hydraulic models, requiring specialized training for operators and technicians.
Dependence on Electricity: Electric press brakes rely entirely on electricity for operation, which means they may be susceptible to downtime in case of power outages or electrical issues.
Hydraulic vs Electric Press Brake: How To Select
Selecting between hydraulic and electric press brakes depends on various factors including your specific application requirements, budget, production volume, and desired features. First of all, we need to have a basic understanding of the difference between the two, including their respective characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, and application scenarios.
1.Precision and Stability
Electric press brakes rely on electric motors and transmission systems for precision. The stability and precision depend on the electric motor's performance and the transmission system's accuracy. While efficient and flexible, they may slightly lag in precision compared to hydraulic press brakes due to limitations in dynamic response and pressure control.
Hydraulic press brakes are known for their powerful stability and precision. The hydraulic system provides continuous and stable power output, crucial for long periods of continuous operation. Hydraulic systems can precisely control motion by adjusting pressure and flow, ensuring high stability even with high precision requirements.
2.Efficiency and Production Capacity
Electric press brakes offer flexible operating speeds and high processing capacity. Their electric motor-driven transmission enables quick start-up and stop, enhancing production efficiency. They can adapt quickly to different metal sheet sizes and shapes, making them efficient for small batch or medium-sized part production.
Hydraulic press brakes excel in handling large and thick metal sheets and are efficient in mass production scenarios. Their continuous, stable power output allows for strong bending capabilities. Equipped with automated control systems, they ensure high production efficiency and quality stability in mass production.
3.Cost and Maintenance
Electric press brakes have lower initial investment and maintenance costs. Their simpler electric motor and transmission systems reduce manufacturing and maintenance expenses. Operations and maintenance are relatively simple compared to hydraulic systems, making them cost-effective for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Hydraulic press brakes have higher production efficiency and stability but come with higher maintenance costs due to the complexity of the hydraulic system. Maintenance involves specialized support, hydraulic oil replacement, and filtration, justified by their advantages in processing large sheets and mass production.
4.Applicable Scenarios
Electric Press Brake:
- Small-scale processing workshops requiring frequent die changes.
- Scenarios requiring high precision where slight lag is acceptable.
- Can be integrated into automated production lines for enhanced efficiency.
Hydraulic Press Brake:
- Large-scale sheet metal processing, especially thick sheets.
- Mass production environments requiring continuous operation.
- Automated production lines for enterprises with high efficiency and quality demands.
Recommendations and Conclusions
In conclusion, both electric press brakes and hydraulic press brakes offer unique advantages and disadvantages, catering to different production requirements and application scenarios. Here's a refined version:
Electric press brakes are preferred for their efficiency, energy efficiency, ease of maintenance, and environmental friendliness, especially in scenarios requiring rapid die changes, precise control, and environmental considerations. However, they may have limitations when handling large tonnage and high-strength materials.
On the other hand, hydraulic press brakes are renowned for their powerful output, wide applicability, and adaptability to complex environments. They excel in scenarios requiring large tonnage, high loads, and precise control, such as bending large metal sheets. However, hydraulic press brakes have higher maintenance costs, energy consumption, and potential environmental issues like hydraulic oil leaks.
When choosing a press brake, enterprises should consider their specific production requirements comprehensively. For companies prioritizing efficiency, precision, and environmental awareness, electric press brakes may be preferable. For scenarios requiring handling of large, high-strength materials, where cost and environmental requirements are less strict, hydraulic press brakes may be more suitable.
Key Considerations For Choosing Electric Press Brake
- Heavy-Duty Applications: Choose hydraulic press brakes if you primarily work with large and thick metal sheets requiring high bending force and stability.
- Mass Production: Hydraulic press brakes are ideal for mass production scenarios where continuous operation and high efficiency are crucial.
- Versatility: If your work involves bending a wide range of materials and thicknesses, hydraulic press brakes offer versatility and can handle diverse tasks effectively.
- High Precision: Hydraulic press brakes are suitable for applications demanding high precision and consistent bending results, especially with large parts.
- Initial Investment: Be prepared for a higher initial investment compared to electric press brakes, but consider it if your production demands justify the expense.
- Maintenance: Hydraulic press brakes require more maintenance due to their hydraulic systems, but they offer robust performance for heavy-duty applications.

Key Considerations For Choosing Hydraulic Press Brake
- Flexibility and Quick Setup: Electric press brakes are suitable for environments requiring frequent die changes or setups due to their faster setup times and flexibility.
- Precision Parts: If your work involves precision parts where slight lag in precision is acceptable, electric press brakes can provide accurate results.
- Small to Medium Production Runs: Electric press brakes are efficient for small to medium batch production due to their quick start-up and stop times.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric press brakes consume electricity only during operation, making them more energy-efficient compared to hydraulic systems.
- Lower Initial Cost: If you have budget constraints or operate a small workshop, electric press brakes usually have lower initial costs and maintenance requirements.
- Ease of Maintenance: Electric press brakes generally have simpler maintenance
World-renowned Press Brake Manufacturers
Several manufacturers are renowned for producing high-quality electric and hydraulic press brakes used worldwide. Here are some of the world-renowned press brake manufacturers:
- Amada:
- Amada is a leading manufacturer of sheet metal machinery, including press brakes.
- They offer a wide range of hydraulic and servo-electric press brakes known for their precision, reliability, and innovative features.
- Trumpf:
- Trumpf is known for its advanced machine tools, including press brakes.
- Their TruBend series offers hydraulic and electric press brakes with state-of-the-art CNC control and automation capabilities.
- Bystronic:
- Bystronic manufactures high-quality press brakes known for their precision bending and efficiency.
- Their Xpert and Xcite series feature innovative technology for bending various materials and thicknesses.
- LVD Company:
- LVD is a well-established manufacturer of sheet metalworking machinery, including press brakes.
- Their Synchro-Form and Easy-Form series offer hydraulic press brakes with advanced bending technology.
- Durma:
- Durma is a global manufacturer of sheet metal machinery, including press brakes.
- They offer a wide range of hydraulic and servo-electric press brakes known for their performance and reliability.
- Krrass:
- Krrass is known for its versatile range of press brakes suitable for various bending applications.
- Their MB8 and PBS series are widely used for precision bending.
- Accurpress:
- Accurpress manufactures hydraulic press brakes known for their durability and accuracy.
- They offer a range of models suitable for different production needs.
- Baykal:
- Baykal is a prominent manufacturer of sheet metal machinery, including press brakes.
- Their press brakes are known for their robust construction and advanced features.
- Salvagnini:
- Salvagnini is recognized for its innovative bending solutions and automation technology.
- Their press brakes offer advanced bending capabilities and integration with automated systems.
- Ermaksan:
- Ermaksan produces a range of hydraulic and servo-electric press brakes known for their quality and performance.
- Their machines are suitable for various bending applications.

Which Is Better? Knock Krrass Machinery For The Answer
Regardless of your preference, Krrass has a comprehensive range of metal press brakes and similar tools to meet your needs. We recommend carefully evaluating your specific requirements, such as the types of materials you will be working with, the size of your workshop, and your budget. By thoroughly assessing these factors, you can make an informed decision on the press brake that best suits your operation.
Browse our entire catalog of press brake machines and let us know if you have any questions!