Machinists use laser cutting and plasma cutting interchangeably. However, while they perform similar cutting functions, they are different in their applications and principles. These two cutting techniques have been around since the 20th century, but machinists have modernized them for more effective uses.
Here, you’ll learn the differences between plasma cutting vs laser cutting. You’ll also learn the advantages of the two cutting methods plus how to determine which to use.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a cutting technology that slices materials by the use of amplified laser light. This technique was introduced in the mid-1960. Laser cutting has a high precision rate, and this is because it is not a manually performed process. Instead, a computer controls it, such as a computer numerical control (CNC).
Using laser light for cutting is not rocket science; it is instead a simple process. It involves focusing laser light into a small point using optics. The laser light becomes smaller and hotter as it enters the optics. This increase in temperature melts and cuts through the workpiece, and the computer directs the whole process. However, rather than melting, some objects will either burn, blown off by a jet of gas, or vaporized away. This leaves the edge smooth with a high-quality surface finish.
There are three significant types of lasers used in laser cutting. They are Carbon dioxide (CO2), neodymium (Nd), and yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Nd:YAG). Each of these lasers is suitable for different purposes. CO2 is best for cutting, boring, and engraving.
However, if you need a laser for boring where high energy and low repetition is required, Nd is right for you. Nd:YAG, on the other hand, is suitable for boring and engraving where you need high power. Therefore, both Nd and Nd:YAG are identical in style but used for different purposes. One thing that these three primary types of lasers have in common is that they all use an amplified laser to cut workpieces.
What is Plasma Cutting?
Machinists have been using plasma cutting for decades and still in excellent use today. It originated in the 1950s and is one of the best cutting methods ever since. The process involves cutting through electrically conductive materials using an accelerated jet of hot plasma. This hot plasma can melt through any materials regardless of how tough it is.
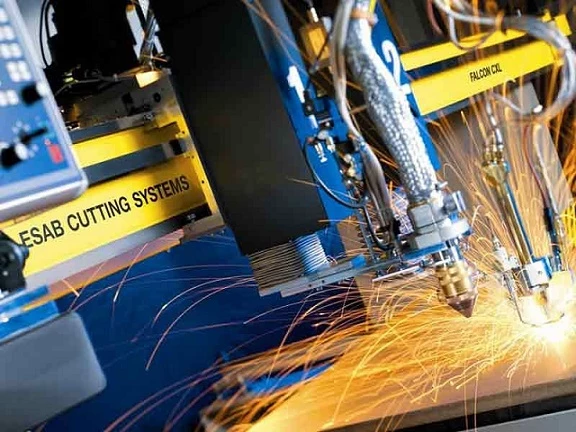

Plasma cutting only works for electrically conductive materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, steel, brass, and copper. It doesn’t use naked flame; instead, it uses plasma, a conductive ionized gas. Plasma is usually very hot during the cutting process. However, the type of plasma torch used generally determines the temperature. The torch produces varying temperatures, but the temperatures are usually very hot.
Plasma can reach a very high temperature up to 40,000 degrees Fahrenheit. Plasma torches, combined with precision CNC control, can produce parts that require little or no finishing. These torches emit radiation, which can be harmful to humans; therefore, workers must protect themselves against eye arc by wearing protective glasses or goggles.
Differences Between Laser Cutting and Plasma Cutting
When considering plasma cutting vs laser cutting, we have to look at the two major areas where the two cutting methods differ. They are:
Difference in Principle
Plasma cutting uses compressed gas, including oxygen, air, inert, and others, depending on the type of material used. This cutting process involves the creation of an artificial channel of plasma through the workpiece. The plasma will be at a very high temperature, and with such temperature, it can melt, evaporate or burn through any object, no matter how thick.
Laser cutting, on the other hand, uses laser beams generated by laser devices. A series of reflectors transmit the laser beams. Afterward, the beam is focused on the workpiece by a focus lens. The laser beam will heat and melt the focal point, creating a smooth edge with a high-quality surface finish.
In summary, plasma vs laser cutting differs in principle. Plasma cutting uses plasma, while laser cutting uses amplified laser light.
Application
Machinists use plasma cutting to cut all sorts of metals. However, it is best for cutting the medium thickness plates.
Laser cutting is best for cutting medium-thin plates. The cutting materials are also wide, including metal, non-metal, glass, ceramics, rubber, wood, plastics, PVC, leather, organic glass, textiles, etc.
Therefore, plasma-cut materials have a lower range of choice compared to laser cutting with a broader range. For thin sheet cutting, laser cutting does a better job than plasma cutting.
Machinists use plasma cutting where the following are required: small deformation, small heat affected area, narrow cutting slot, and fast cutting speed.
Laser, on the other hand, is used where the following are required: very high precision, high direction, high intensity, higher speed, and no subsequent processing.
Also, if you compare plasma vs laser cutting cost, plasma cutting is cheaper.
Advantages of Laser and Plasma Cutting
Laser and plasma cutting have their respective advantage, which you should consider when finding the suitable one to use. The advantages of each include:
Laser Cutting Advantages
- It provides a smoother edge that requires no extra finish touches
- A fast-cutting speed that can reach 10m/min for thin sheets
- High precision with a high positioning accuracy that can reach 0.05mm and repositioning accuracy that can reach 0.02mm
- It can cut different materials, including metals, rubber, wood, plastics, PVC, leather, organic glass, textiles, etc.
Plasma Cutting Advantages
- It can cut medium-thick plate at a very high speed
- The maintenance cost of plasma cutting is cheaper
The Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Laser Cutting vs Plasma Cutting
Most people find it challenging to choose a suitable cutting method, mainly because the two methods are similar. However, to avoid the unnecessary confusion of choosing between laser vs plasma metal cutting, you should consider three significant factors. They are:
Material
Plasma cutting has limited application compared to laser cutting. Therefore, if you want to cut materials like metals, rubber, wood, plastics, PVC, leather, organic glass, and textiles, you should opt for laser cutting. On the other hand, if you need to cut any sort of metal, mostly medium thickness plates, the right cutting method is plasma cutting.
Precision
The level of precision needed for the job is also something you should consider. If you need a very high precision cutting, laser cutting is your sure bet.
Cost
It is pointless choosing a particular cutting process if it doesn’t suit your budget. Plasma cutting is cheaper; thus, if you are looking for a budget-friendly cutting method, plasma cutting is right for you.
Conclusion
Plasma cutting and laser cutting are both highly effective cutting methods. They both perform the “cutting function,” but their application and principle differ. While machinists use these two interchangeably, it is unprofessional to randomly pick any of them without first considering the purpose you want to use it for. When you consider your need and compare it with the principles and application of each cutting method, you’ll be able to make a clear decision about the right one to opt for.
However, if you still can’t make up your mind, let us help you.
FAQs
Q: Which plasma cutting gas is the best?
A: Depending on the kind of workpiece you’re cutting, you’ll require different types of gases or a special combination. However, the most recommended gases are nitrogen, compressed air, and oxygen.
Q: How do I know which plasma cutting gas to use?
A: For stainless steel or aluminum cutting, compressed air is sufficient. If you are cutting through mild steel, you should opt for oxygen. Choose Nitrogen if you want to cut metals with a thickness of up to 3 inches, including mild and stainless steel or aluminum.
Learn more about our products, please visit and subscribe to our Youtube channel