The evolution of press brake technology, from manual operations to sophisticated CNC systems, has been like a metamorphosis for the metal fabrication industry, completely transforming the way things are done.
Driven by the fierce winds of global competition, the surging tide of increasing demand for automation, and the unyielding need for greater flexibility, press brake history and future have continuously advanced like a fearless explorer, conquering the complex terrains of modern manufacturing requirements. This progression has not only enhanced precision and efficiency, sharpening the process like a dull blade into a razor-sharp instrument, but also reshaped manufacturing processes and workforce capabilities, much like an expert sculptor molding clay.
In this article, we will embark on a journey through the history of press brake technology - from its early manual methods that were as rudimentary as a primitive tool to today’s advanced CNC systems that are like high-tech wizards. We will examine how these innovations have affected precision, efficiency, and overall productivity in metal fabrication as if they were the magic spells casting a powerful influence.
Additionally, we will shine a spotlight on key innovations and applications across various industries, while also peering into the crystal ball to look ahead at future trends that promise to further transform the field like a visionary predicting the next chapter of a great adventure.
Table of Contents
What is a Press Brake?
A press brake is a machine used in metal fabrication that is like an artist’s hands, bending sheet metal into specific shapes. This process involves clamping the workpiece between a top tool, known as the punch, which is like a mighty hammer, and a bottom die that serves as the anvil.
By applying force, the press brake bends the metal to the desired angle, enabling precise shaping of metal components as if it were a magician conjuring the perfect form. This precision is crucial for a wide range of fabrication tasks, from creating simple brackets that are like the building blocks of a structure to complex automotive parts that are the intricate gears of a mechanical masterpiece.
Basic Components of a Press Brake
Understanding the basic components of a press brake is essential for grasping its operation and capabilities, much like knowing the parts of a complex machine:
- Two C-frames - These are positioned on either side of the machine like the sturdy pillars of a gateway, providing structural support. They ensure stability during the bending process, which is vital for keeping accuracy and safety as if they were the unshakable foundations of a castle.
- Movable upper beam - This part controls the movement of the punch like a conductor leading an orchestra. It moves vertically to press the metal against the die, executing the bending action. The precision of this movement is critical for achieving consistent bends, as if it were a tightrope walker keeping perfect balance.
- Table for bottom tool - The table holds the bottom die in place like a steady platform for a precious gemstone. It serves as the stage where the workpiece is clamped and bent. The design and configuration of this table can vary depending on the type of press brake and its intended applications, like various stages for different theatrical performances.
Types of Press Brakes
Press brakes have evolved significantly over time, leading to several types that cater to different manufacturing needs, like a wardrobe with different outfits for various occasions. While not an exhaustive list - the following encapsulates most press brake types:
Manual press brakes
These machines require significant operator skill and physical effort, as if they were old-fashioned manual laborers. They are typically used for simpler tasks or in workshops with lower production volumes, like a small cottage industry. Manual press brakes are ideal for small-scale operations where precision is not as critical, and they provide a cost-effective solution for basic bending needs, like a simple tool for a DIY enthusiast.
Hydraulic press brakes
Introduced in the 1960s, hydraulic systems offer greater flexibility and control over ram speeds and stroke lengths like a skilled driver maneuvering a powerful vehicle. This allows for more precise bending operations compared to mechanical systems. Hydraulic press brakes are known for their ability to manage heavy-duty tasks and are widely used in industries that require robust performance and high force capabilities, like the construction industry building towering skyscrapers.
CNC press brakes
These use Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems to automate bending processes like a robotic assistant taking over repetitive tasks. CNC press brakes are highly efficient, offering unparalleled precision and repeatability by using advanced software to manage bending sequences as if it were a maestro conducting a symphony. They are suitable for complex and high-volume production environments, providing significant reductions in setup times and material waste, like a well-oiled production line in a factory.
Electric press brakes
Also known as servo-electric press brakes, these machines use electric motors to drive the bending process like a quiet and efficient electric engine powering a vehicle. They are energy efficient as they only consume power during the bending operation, unlike hydraulic systems that require continuous power like a thirsty beast. Electric press brakes provide precise control over the bending process, resulting in higher accuracy and repeatability, like a skilled archer hitting the bullseye every time. They are also quieter and have lower maintenance requirements due to the absence of hydraulic fluids, making them ideal for environments focused on sustainability and operational efficiency, like a peaceful and green oasis in the manufacturing desert.
Hybrid press brakes.
These machines combine the benefits of both hydraulic and electric systems like a hybrid animal with the best traits of two species. Hybrid press brakes use a combination of electric motors and hydraulic systems to provide power, offering the precision and energy efficiency of electric models while keeping the high force capabilities of hydraulic systems. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, balancing energy efficiency with the ability to manage demanding tasks, like a versatile athlete excelling in multiple sports. Hybrid systems are particularly helpful in settings where both performance and eco-friendliness are priorities, like a modern and responsible manufacturing facility.
Press Brake History and Future
The evolution of press brakes, from their humble beginnings as manual tools in the 19th century to today’s advanced CNC systems, reflects the industry's relentless drive for precision, speed, and flexibility like a marathon runner chasing the finish line. Over the decades, press brake technology has undergone several key transformations, each contributing to the enhanced efficiency and adaptability that modern metal fabrication demands, like the growth rings of a tree adding strength and resilience over time. From the introduction of hydraulic systems in the 1960s that were like a sudden gust of fresh air to today’s highly automated CNC technology that is the innovative sword of modern manufacturing, these innovations have fundamentally reshaped how manufacturers approach bending operations.
The Birth of Mechanized Metal Bending
The origins of press brakes can be traced back to the late 19th century. The first cornice brake, patented in 1882, was a manually run tool that clamped sheet metal and bent it in a straight line, like a simple but effective pair of pliers. This marked the birth of mechanized metal bending. While rudimentary by today’s standards, these early machines were groundbreaking at the time, as they allowed for more systematic and repeatable bending processes compared to purely manual methods, like the first step on a long journey of progress.
Manual Bending Tools
These early brakes relied heavily on operator skill and physical effort, as if they were the sole artisans shaping the metal. Operators would manually position the workpiece and apply force to bend it over a fixed die, like a craftsman using his hands and muscles. While effective for simple tasks, these machines had significant limitations in terms of speed, precision, and repeatability, like a slow and imprecise old-fashioned clock.
First Steps Toward Automation
Even in this early phase, there was a growing recognition of the need for more efficient bending solutions, like a faint glimmer of light in the darkness. The limitations of manual brakes led to further experimentation and paved the way for more advanced mechanical systems that would appear in the early 20th century, like the first buds of spring heralding a new season of growth.
Advancements in the Early 20th Century
The early 20th century saw considerable progress with the development of mechanical press brakes. These machines could achieve up to 30 strokes per minute—an impressive feat at the time—and significantly boosted production speed and efficiency like a turbocharger for manufacturing.
Mechanical Press Brakes
Mechanical press brakes introduced motorized systems that allowed for faster operation compared to manual models, like a horse-drawn carriage evolving into a motor car. These machines used flywheels and mechanical linkages to deliver consistent force with every stroke, making them ideal for mass production environments like a factory churning out products on an assembly line.
Impact on Industrial Growth
This leap in technology aligned perfectly with the industrial boom of the early 1900s. Industries like automotive manufacturing and construction were expanding rapidly, and mechanical press brakes provided manufacturers with the capacity to meet growing demand for mass-produced metal components like a key that unlocked the door to industrial expansion.
The Hydraulic Revolution of the 1960s
A breakthrough in press brake technology came during the 1960s with the introduction of hydraulic press drives. This innovation offered unprecedented flexibility in controlling ram speeds, pressure, and stroke lengths—capabilities that were previously unattainable with mechanical systems like a new superpower discovered.
Hydraulic Systems: A Game-Changer
Hydraulic press brakes allowed operators to finely tune bending parameters such as force and speed, which was crucial for achieving more complex bends with greater precision like a skilled chef adjusting the heat and ingredients for a perfect dish. This was particularly beneficial for just-in-time manufacturing processes that were gaining traction during this period like a new trend catching on.
Precision and Flexibility in Manufacturing
The advent of hydraulic systems did more than just increase precision; it eased a shift from mass production to more customized production models like a rigid path diverging into multiple flexible routes. Manufacturers could now produce small batches of bespoke parts without sacrificing efficiency or quality, like a tailor making custom-made suits. This flexibility also helped reduce material waste and improved overall product quality like a careful gardener pruning away the unnecessary to let the best bloom.
Laying the Groundwork for CNC Systems
The introduction of hydraulic systems set the stage for even greater advancements in press brake technology—most notably, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems. CNC technology revolutionized press brake operations by providing an unparalleled level of precision and automation like a quantum leap into a new era.
CNC: The Dawn of Automation
CNC systems brought about a new era of automated bending processes. By using pre-programmed instructions, CNC press brakes could execute highly intricate and consistent bends with minimal human intervention like a self-playing piano following a musical score. This was a meaningful change for industries requiring high precision and repeatability, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing like a perfect tool for the most delicate of surgeries.
As we look ahead, advancements such as AI integration and Industry 4.0 connectivity promise to further enhance press brake capabilities, ensuring that this essential tool stays at the forefront of industrial manufacturing for years to come like a shining star guiding the way.
CNC Press Brakes: The Birth of Exceptional Change
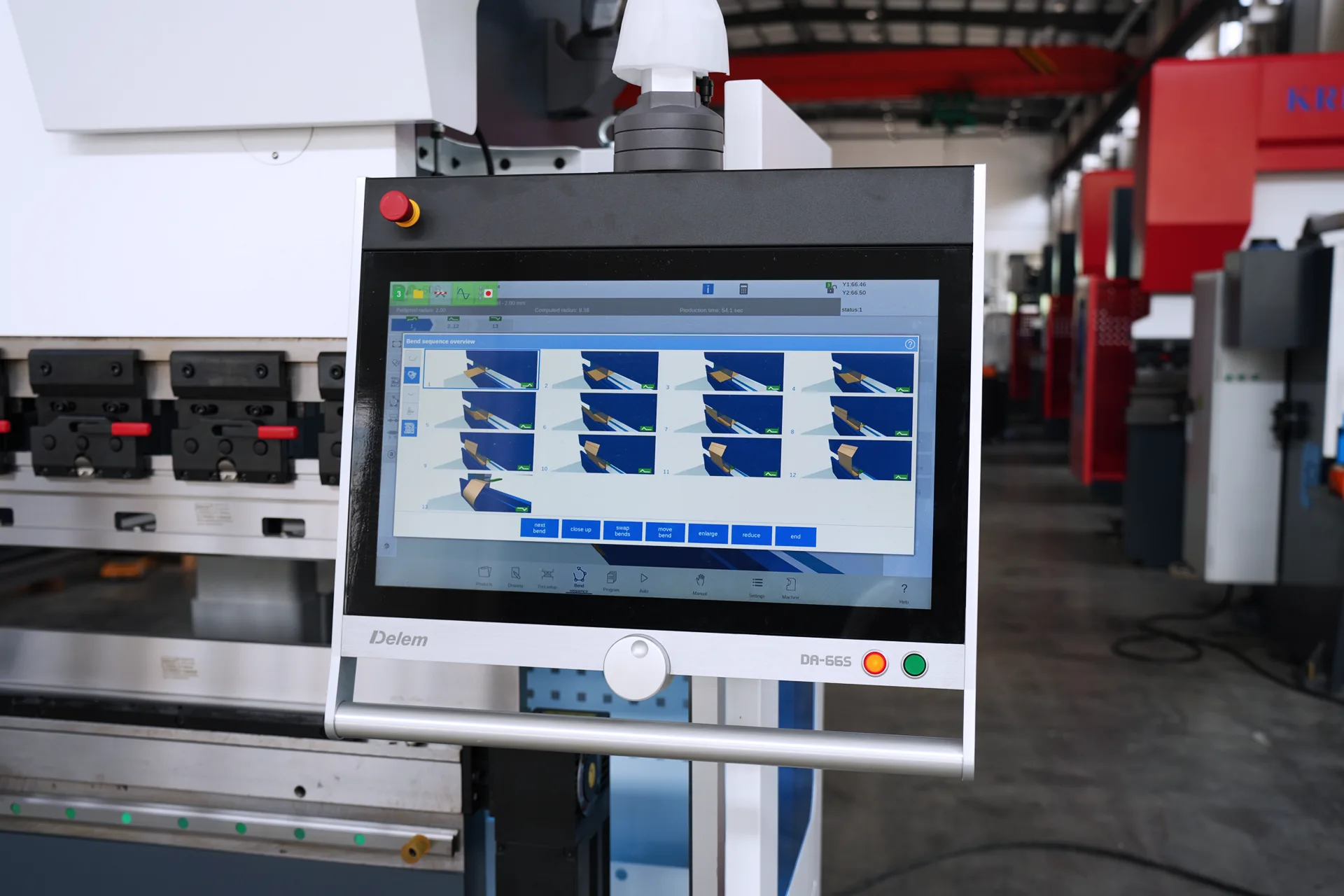

Since their introduction in the late 1970s, CNC press brakes have undergone significant evolution, continually pushing the boundaries of metal forming like a fearless pioneer exploring uncharted territories. The integration of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems has transformed metal fabrication by offering greater precision, efficiency, and automation like a magic wand that transforms the ordinary into the extraordinary. These advancements have redefined how manufacturers approach bending operations, making CNC press brakes indispensable in modern production environments like a trusty sidekick in a heroic adventure.
Adaptive Bending Technology
CNC press brakes today use advanced software and hardware to achieve high accuracy and repeatability like a finely tuned instrument. One of the most notable innovations is adaptive bending technology, which uses real-time feedback to dynamically adjust bending parameters during operation like a navigator constantly adjusting the course. This ensures consistent bend angles by compensating for variations in material properties like thickness or hardness like a skilled acrobat adjusting to different surfaces.
Real-Time Feedback Systems
Adaptive bending technology relies on force measurement and position feedback sensors to check the bending process in real time like a vigilant watchdog. These sensors detect deviations in material properties and automatically adjust the ram's force or position to keep precision like a self-correcting mechanism. This capability reduces the need for manual adjustments and trial bends, significantly improving production efficiency like a well-oiled machine running smoothly.
Material Compensation
Material inconsistencies—such as varying thicknesses or hardness—can lead to inaccurate bends like a bumpy road causing a car to swerve. Adaptive systems automatically compensate for these variations, ensuring each bend meets exact specifications without operator intervention like a skilled driver smoothly navigating through rough terrain. This technology is particularly valuable in industries where precision is critical, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing like a life-saving device that must be perfect.
3D Modelling and Offline Programming
The integration of 3D modelling and offline programming capabilities has revolutionized how operators prepare for bending operations like a new map guiding the way. These tools allow operators to simulate bending processes before production begins, reducing setup times and material waste like a rehearsal before a performance.
CAD/CAM Integration
Advanced CAD/CAM software enables seamless transfer of design data from digital models to CNC press brakes like a teleportation device for information. Operators can create complex part geometries in CAD software, simulate the entire bending sequence offline, and then upload the program directly to the machine like a conductor passing the musical score to the orchestra. This cuts manual programming errors and reduces lead times like a shortcut on a long journey.
Simulation Benefits
By simulating bends before production, operators can find potential issues—such as tool collisions or incorrect bend sequences—before they occur on the shop floor like a weather forecast warning of a storm. This initiative-taking approach minimizes downtime and material waste while ensuring that parts are produced correctly on the first attempt like a perfect shot on goal.
Laser-Based Angle Measurement
Laser-based angle measurement systems are increasingly common in high-end CNC press brakes like a precious jewel adorning a crown. These systems provide real-time feedback on bend angles, allowing for automatic adjustments to achieve precise results like an expert shooter using a scope to hit the target.
Precision in Complex Operations
Laser-based systems are particularly beneficial for complex bending operations that require tight tolerances like a tightrope walker performing in a high-wind environment. By continuously checking the bend angle during operation, these systems ensure that even intricate parts meet exact specifications without requiring manual measurement or adjustment like a self-steering ship on a precise course.
Automatic Adjustments
When deviations from the desired angle are detected, laser-based systems automatically adjust the ram position or force to correct the bend in real time like a self-correcting compass. This level of automation enhances both speed and accuracy, making it ideal for industries like automotive manufacturing where consistency is paramount like a well-choreographed dance routine.
Industry 4.0 Integration
The advent of networked CNC press brakes has eased Industry 4.0 integration like a bridge connecting different islands. These machines can communicate with other manufacturing systems, sharing data on production rates, machine status, and quality control metrics like a social network for machines.
Real-Time Data Sharing
Industry 4.0-enabled press brakes can send real-time data to centralized control systems or cloud-based platforms like a messenger delivering important news. This connectivity allows manufacturers to check machine performance remotely, track production metrics, and implement predictive maintenance strategies based on actual usage data like a doctor using a patient’s vital signs to predict health issues.
Predictive Maintenance
By analyzing data from connected machines, manufacturers can predict when components—such as hydraulic pumps or tooling—are likely to fail like a fortune-teller seeing into the future. This initiative-taking approach reduces unexpected downtime and extends equipment lifespan by ensuring maintenance is performed only, when necessary, like a well-timed visit to the mechanic.
Energy Efficiency Innovations
Recent developments have also focused on energy efficiency, with hybrid and all-electric models reducing energy consumption compared to traditional hydraulic systems like a fuel-efficient car saving gas.
Hybrid Systems
Hybrid press brakes combine electric motors with hydraulic systems to deliver high force while using less energy than conventional hydraulic-only machines like a hybrid animal that is both strong and efficient. These models offer energy savings of up to 50%, making them both cost-effective and environmentally friendly like a double win in a game.
CNC Press Brakes: The Impact on the Manufacturing Sector
The introduction of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) press brakes has revolutionized the metal fabrication industry by dramatically improving productivity, precision, and operational efficiency like a powerful engine driving a vehicle forward. These advanced machines have transformed traditional manufacturing processes into highly automated workflows that deliver consistent quality at scale like a factory that never makes a mistake.
Enhanced Production Speed
CNC press brakes significantly increase production speed through automated controls and pre-programmed bending sequences like a race car on a high-speed track. This allows manufacturers to manage larger volumes of work while meeting tight deadlines like a busy chef cooking multiple dishes at once.
Automated Workflow
With CNC technology automating most of the bending process, operators can focus on loading materials while the machine executes pre-programmed sequences with minimal supervision like a captain delegating tasks on a ship. This automation enhances throughput and reduces operator fatigue like a helping hand in a tiring task.
Multi-Part Production
CNC press brakes can switch between different part programs quickly without requiring extensive retooling or setup changes like a versatile actor changing roles. This flexibility makes them ideal for manufacturers producing multiple part types within a single production run like a factory that can produce assorted products on the same assembly line.
Precision and Quality
Modern CNC systems achieve exceptional ram repeatability through advanced sensors and control mechanisms like a sniper hitting the same spot every time. This ensures consistent bends across large production runs like a uniform pattern in a fabric.
Ram Repeatability
CNC press brakes offer ram repeatability within microns due to their precise control over ram movement during each stroke like a watchmaker assembling a delicate timepiece. This ensures that every part is bent exactly as programmed—even across thousands of cycles—minimizing scrap rates due to inaccurate bends like a perfectionist ensuring every detail is correct.
High-Precision Components
Industries such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing rely heavily on CNC press brakes because they need components with extremely tight tolerances like a space shuttle needing perfect parts. The precision offered by these machines ensures that critical parts meet stringent quality standards consistently like a dependable guardian protecting the highest standards.
Streamlined Setup and Integration
CNC press brakes significantly reduce setup times by quickly switching between stored bending programs like a magician changing tricks in an instant. This streamlines operations and reduces downtime like a traffic jam clearing up. Furthermore, the seamless integration between CAD/CAM software and CNC controls cuts manual programming errors by allowing operators to import digital designs directly into the machine’s interface like a direct connection between two minds. This reduces setup time dramatically while ensuring correct execution from start to finish like a flawless performance.
Modern Press Brakes
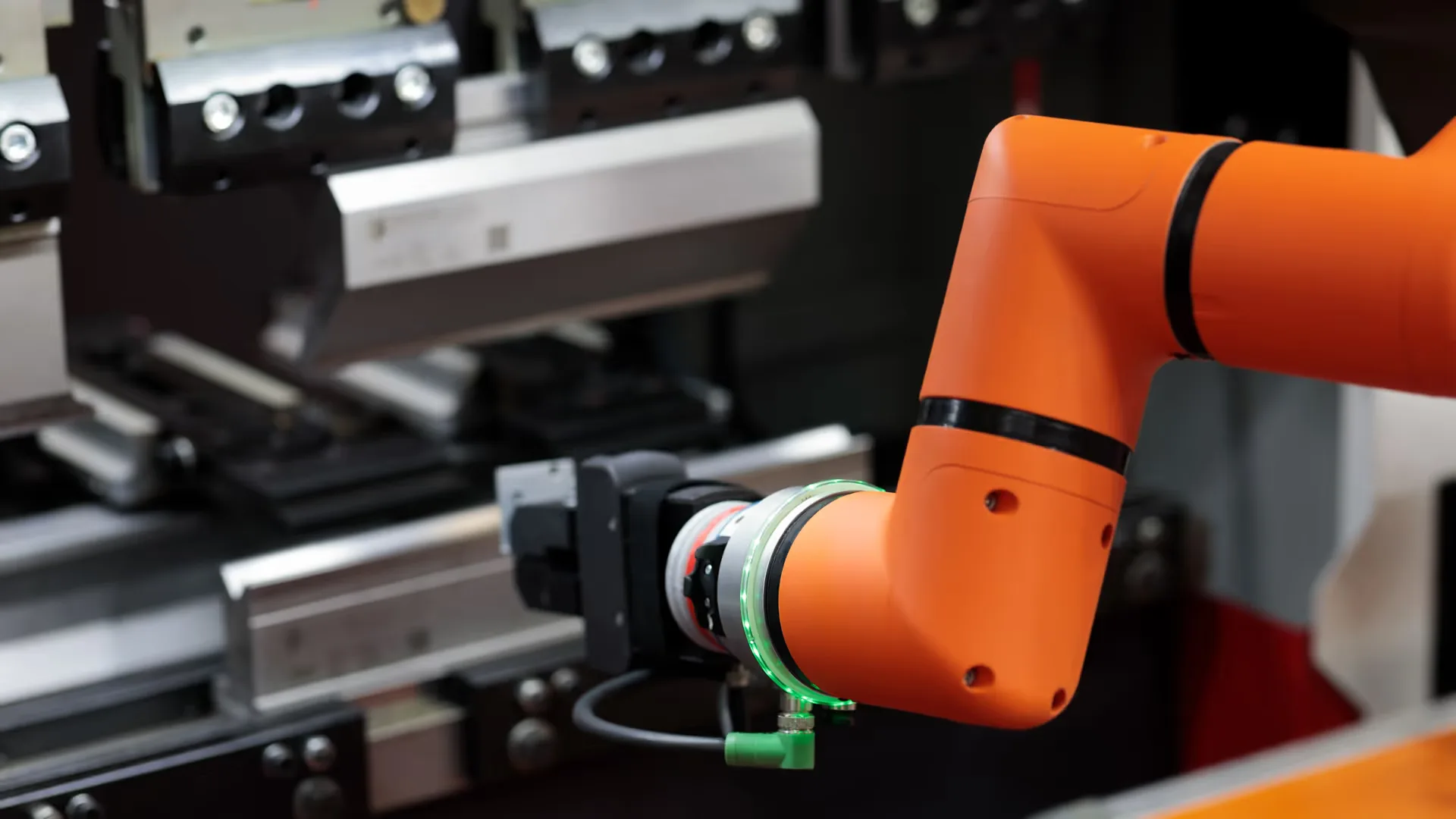

Modern press brakes have achieved remarkable advancements in precision and efficiency, significantly enhancing their capabilities compared to earlier models like a student graduating with honors. Here are the key factors contributing to these improvements:
Precision of Modern Press Brakes
Modern press brakes have made significant strides in achieving exceptional accuracy, thanks to advancements in technology and engineering like a runner breaking world records. These machines are now equipped with features that ensure consistent and precise bending, meeting the high demands of various industries as if they were precision instruments calibrated to perfection.
Advanced Press Brake Control Systems
Modern press brakes use sophisticated control systems that enable precise adjustments during the bending process, like an expert pianist delicately hitting the right keys. These systems often incorporate real-time feedback mechanisms that allow for dynamic corrections, ensuring consistent results even with variations in material properties as if they were a skilled navigator adjusting the ship's course in changing seas. This level of precision is crucial for industries where exact specifications are necessary to keep quality and functionality, like a watchmaker crafting a luxury timepiece where every millimeter matters.
Laser-Based Angle Measurement
Many high-end press brakes now feature laser-based angle measurement systems, like a lighthouse guiding ships in the dark. These systems provide real-time data on bend angles, allowing for automatic adjustments to achieve precise results like an expert shooter zeroing in on a target. This technology is particularly beneficial for complex bending operations with low tolerance thresholds, such as those found in aerospace and medical device manufacturing, where the slightest deviation can be like a single wrong note in a symphony.
Adaptive Bending Technology
This innovation uses force measurement and position feedback to adjust bending parameters on the fly, compensating for variations in material properties like thickness or hardness like a chameleon adapting to its surroundings. Some systems can achieve impressive bend angle accuracies without operator intervention, significantly reducing the need for trial bends and adjustments like a self-driving car smoothly navigating through traffic. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces material waste and production time, making it a valuable feature for high-volume manufacturing environments like a well-oiled production line humming with productivity.
Efficiency of Modern Press Brakes
With increasing competition in the manufacturing landscape, efficiency is a key driver of success like a powerful engine propelling a vehicle forward. Modern press brakes have evolved significantly, incorporating innovative technologies that enhance productivity and reduce operational costs like a magician pulling rabbits out of a hat. These advancements make them indispensable tools in metal fabrication, allowing manufacturers to meet the demands of various industries with speed and precision like a champion athlete competing in multiple events.
Automation and CNC integration
The integration of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems has transformed press brake operations by automating bending sequences like a robotic factory worker tirelessly performing tasks. This automation reduces setup times and minimizes human error, leading to faster production cycles and higher throughput like a conveyor belt moving products at a rapid pace. CNC systems allow for precise control over the bending process, enabling manufacturers to manage complex designs with ease and consistency like a skilled artist painting a detailed masterpiece.
Energy-efficient models
Recent developments have focused on energy efficiency, with hybrid and all-electric press brakes offering energy savings of up to 50% compared to traditional hydraulic systems like a miserly spender conserving every penny. These eco-friendly options reduce operational costs and align with growing environmental concerns in manufacturing like a green flag waving for sustainability. By consuming less energy, these models contribute to sustainability goals while keeping high performance levels like a well-balanced athlete excelling in both speed and endurance.
Tandem systems and specialized Tooling
Tandem press brake systems enable the bending of exceptionally long parts with high precision by synchronizing multiple machines to work in unison like a synchronized swimming team performing flawlessly. This capability is crucial for industries requiring large-scale components, such as construction and shipbuilding, like a crane lifting heavy loads with precision. Additionally, specialized tooling like Multi-V dies allows for a wide range of bend radii with a single tool, reducing the need for frequent tool changes and enhancing operational efficiency like a multitasking tool that can manage various jobs.
These advancements in precision and efficiency have expanded the applications of press brakes across various industries, from aerospace components requiring tight tolerances to architectural panels demanding consistent aesthetics like a versatile actor fitting into distinct roles. Modern press brakes meet increasingly stringent requirements while improving productivity and reducing waste, making them indispensable tools in contemporary metal fabrication like a dependable partner in a successful business.
KRRASS's Legacy and Press Brake Innovations
KRRASS, a Chinese manufacturer founded in 1998, has consistently proved its prowess in the metal fabrication industry through groundbreaking innovations and a commitment to quality like a trailblazer carving a new path. Over the past two decades, KRRASS has appeared as a serious market player, influencing the evolution of press brake technology and setting new standards in the industry like a trendsetter leading the fashion.
A Continuing Tradition of Excellence
KRRASS's journey began with a focus on crafting high-quality sheet metal working machinery, like an expert craftsman dedicated to his trade. Since its establishment, KRRASS has always prioritized safety and performance standards synonymous with European engineering like a student aiming for the highest academic standards. This commitment to excellence has earned KRRASS numerous accolades and set up its reputation as a leader in the global market like a champion winning multiple trophies.
Pioneering innovations
- Advanced automation - The PBS series from KRRASS is renowned for its advanced automation capabilities, including robotic aid and laser angle measuring devices like a high-tech superhero with powerful gadgets. These features enhance precision and productivity, enabling complex bending processes with minimal human intervention like a conductor leading an orchestra with effortless grace.
- Energy efficiency innovations - Responding to the global demand for sustainable manufacturing solutions, KRRASS's PBE-Hybrid Press Brakes are engineered for low energy consumption like a fuel-efficient car designed for the future. These machines not only reduce operational costs but also align with efforts to minimize industrial carbon footprints, highlighting KRRASS's commitment to environmental responsibility like a guardian of the planet.
- Customization and flexibility - KRRASS press brakes are equipped with sophisticated CNC systems that allow for elevated levels of customization like a tailor-made suit designed to fit perfectly. This flexibility enables quick programming and easy adjustments, making them ideal for handling small batch sizes and frequent design changes like a versatile tool that can adapt to any situation.
Comprehensive product range
Beyond press brakes, KRRASS offers a wide array of metal fabrication equipment, including shears, notches, punching machines, laser cutting systems, plasma cutting machines, and vertical machining centers like a one-stop shop for all metalworking needs. This comprehensive product range allows KRRASS to provide integrated solutions that streamline manufacturing processes and enhance operational efficiency like a well-coordinated team working towards a common goal.
Global reach and influence
With a distribution network spanning over 100 countries, KRRASS has facilitated the widespread adoption of its advanced press brake technologies worldwide like a spreading wildfire. This international presence not only expands KRRASS's influence but also contributes to the global dissemination of innovative metal-forming techniques like a messenger spreading good news. By keeping a strong foothold in both domestic and international markets, KRRASS continues to drive advancements in the industry like a powerful engine driving progress.
Awards and recognition
KRRASS's dedication to innovation and quality has been recognized through various awards and accolades over the years like a star being awarded for outstanding performance. These honors underscore KRRASS's role as a pioneer in metal fabrication technology and its ongoing contribution to advancing industry standards like a torchbearer leading the way.
KRRASS's legacy is built on a foundation of innovation, quality, and global reach. As a serious market player, KRRASS continues to set benchmarks in press brake technology, ensuring that it stays at the forefront of the metal fabrication industry like a leader standing at the head of the pack.
Advanced Questions & Answers

In this FAQ section, we take a deeper look into the technical aspects of KRRASS's press brakes, addressing frequent questions that arise when selecting and running these advanced machines like a detective solving a mystery. Whether you're looking to understand the benefits of CNC automation or explore how KRRASS's energy-efficient models can reduce operational costs like a wise investor seeking the best returns.
What are the main differences between manual and CNC press brakes?
Manual press brakes require significant operator skill and physical effort, relying on manual adjustments to achieve desired results like a traditional blacksmith working with a hammer and anvil. In contrast, CNC press brakes, like KRRASS's PBS series, use computer-controlled systems to automate and perfect the bending process like a modern factory using automated robots. This results in higher precision, repeatability, and efficiency, allowing for complex bends with minimal human intervention like a skilled surgeon performing a delicate operation. KRRASS's CNC systems also offer advanced features like CNC crowning and laser-based angle measurement, ensuring consistent accuracy across all bends like a precision-guided missile hitting its target every time.
How do CNC press brakes improve production efficiency?
KRRASS's CNC press brakes significantly enhance production efficiency by automating bending sequences and reducing manual setup times like a well-oiled machine running smoothly. The integration of Delem controllers allows operators to pre-program complex bending operations, which reduces downtime between jobs and cuts trial-and-error adjustments like a well-rehearsed play with no mistakes. Additionally, KRRASS's machines feature quick release clamping systems and multi-axis back gauges, enabling rapid tool changes and precise material positioning, further streamlining workflows like a NASCAR pit crew working with lightning speed.
What role does software play in KRRASS's CNC press brakes?
Software is integral to the functionality of KRRASS's CNC press brakes like a brain is to a body. The Delem DA-66S and DA-69S controllers provide comprehensive control over bending operations, offering 2D/3D visualization, automatic bend sequence calculations, and collision detection like a high-tech control center guiding a spaceship. This software allows operators to simulate bending processes before production begins, reducing errors and material waste like a dress rehearsal before a big performance. Additionally, offline programming capabilities enable operators to prepare jobs while the machine is running another task, maximizing uptime like a multitasking superhero.
What advanced safety features do KRRASS press brakes offer?
KRRASS prioritizes safety without compromising performance like a cautious driver who still drives efficiently. The PBS series comes optional with the MSD safety system, which uses a multi-point laser sensing device to protect operators during bending tasks like a vigilant guardian angel. For enhanced safety, the optional DSP laser protection system offers motorized finger guards that ensure operator protection while keeping high productivity levels like a fortress protecting its inhabitants while still allowing for normal activities. These systems are designed to meet stringent EU safety standards, providing peace of mind in high-volume production environments like a safety net for a high-wire act.
How do energy-efficient models help my operation?
KRRASS has made significant strides in energy efficiency with its hybrid models, such as the PBE-Hybrid series. These machines combine hydraulic power with servo-electric technology, reducing energy consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional hydraulic systems like a miserly miser cutting down on expenses. This not only lowers operational costs but also aligns with sustainability goals by minimizing carbon footprints like a tree absorbing carbon dioxide. The hybrid system only activates hydraulics when needed for bending operations, making it an ideal solution for manufacturers looking to reduce energy usage without sacrificing performance like a frugal spender who still gets value for money.
How does KRRASS’s adaptive bending technology improve accuracy?
KRRASS’s adaptive bending technology uses force measurement and position feedback systems to dynamically adjust bending parameters during operation like a skilled tightrope walker constantly adjusting for balance. This ensures consistent bend angles by compensating for variations in material properties such as thickness or hardness like a shock absorber smoothing out bumps in the road. With features like laser-based angle measurement, KRRASS’s machines can achieve bend angle accuracies within tight tolerances without requiring operator intervention—making them ideal for industries where precision is critical like a diamond cutter working with precious gems.
What should I consider when selecting a press brake for my business?
When selecting a press brake, consider several factors like a careful shopper evaluating assorted products:
Material type & thickness - Varied materials require varying levels of force for correct bending like different keys fitting different locks.
Bending length & force requirements - KRRASS offers models like the PBS series with bending lengths ranging from 1250mm to 6100mm and forces from 40 to 600 tons. Further, KRRASS is renowned for producing extra-large press brakes that cater to heavy-duty and large-scale metal fabrication needs. With bending capacities ranging up to 6000 tons and bending lengths 7m) and custom options available for even larger tonnages and lengths upon request like a tailor offering custom-made suits for all sizes.
Automation needs - Evaluate whether you need advanced automation features like multi-axis back gauges or robotic aid for material handling like a factory manager deciding on the best production tools.
Production volume - High-volume operations may receive help from hybrid models that offer both energy efficiency and high throughput like a busy highway that needs both speed and fuel efficiency.
Space constraints - Ensure your facility can accommodate the machine's footprint and any added automation equipment like a homeowner making sure a new piece of furniture fits in the room.
How does CNC crowning enhance precision in KRRASS press brakes?
CNC crowning is a standard feature in KRRASS’s PBS series that automatically adjusts for machine deflection during bending operations like a self-leveling platform. This ensures uniform pressure distribution along the die length, resulting in consistent bend angles across the entire workpiece—even on long or thick materials like a perfectly flat tablecloth on a large table. By automating this adjustment process, CNC crowning cuts manual fine-tuning and reduces material waste caused by inaccurate bends like a magic eraser removing mistakes.
How are KRRASS machines tailored for customization and flexibility?
KRRASS’s CNC press brakes are designed with flexibility in mind like a gymnastic routine that can be adapted to different performances. The PBS series includes features like adjustable Z1 + Z2 back gauges for flexible positioning of materials and front sheet followers for handling large or heavy materials like a toolbox with adjustable compartments. These customization options allow businesses to tailor their machines to specific production needs—whether they’re working with intricate components or large-scale industrial projects like a chef using different utensils for different recipes.





Reviewed by 1 user
The controls are intuitive, which minimizes the learning curve, Great Press Brake